Figure 2.
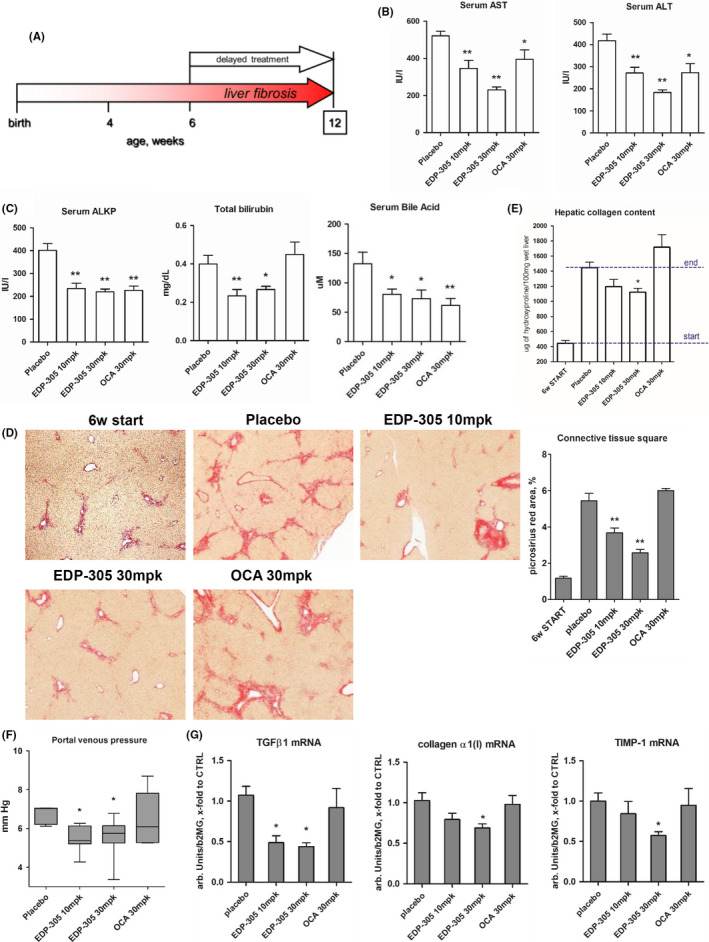
Delayed treatment with EDP‐305 potently suppresses liver injury and fibrosis in BALBc.Mdr2‐/‐ mouse model. (A) BALBc.Mdr2−/− mice with pre‐established advanced liver fibrosis were administered with EDP‐305 (10 mg/kg or 30 mg/kg), OCA (30 mg/kg) or repelleted base chow as placebo control, from 6 to 12 weeks of age (n = 9‐10). WT are healthy untreated wild‐type mice, 6w start group is a ‘start of treatment’ Mdr2‐/‐ controls. (B) Serum levels of transaminases (ALT and AST), and (C) Serum alkaline phosphatase test (ALKP), total bilirubin (TBIL) and bile acid. (D) Representative images of connective tissue (picrosirius red, 50x) staining and morphometric quantification of collagen. (E) Hepatic collagen content (determined biochemically via hydroxyproline content). (F) Portal venous pressure at study end‐point. (G). Profibrogenic transcript levels of procollagen α1(I), TGFβ1, TIMP‐1 as measured by TaqMan qRT‐PCR. Data are mean ± SEM, *P < .05; **P < .01 compared to placebo control group, #, P < .05 compared to start of treatment controls (ANOVA with Dunnett's post‐test)
