Figure 7.
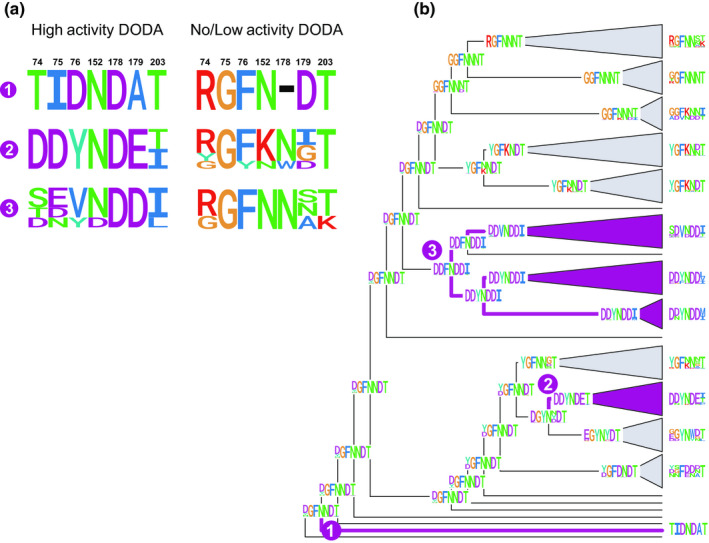
Reconstruction of seven functionally important amino acids on the l‐DOPA 4,5‐dioxygenase (DODA) phylogeny showing a shift in patterns associated with DODA genes of high l‐DOPA 4,5‐dioxygenase activity. (a) Proportional logo plots of the seven residues identified by Bean et al. (2018) across functionally characterised high activity (left) and no or only marginal activity (right) paralogues included in this study. 1: ShDODAα1 vs ShDODAα2 (Stegnospermataceae); 2: CqDODA‐1, BvDODAα1 vs PhybDODAα, BvDODAα2‐5 (Amaranthaceae); 3: McDODAα1, PmDODAα1, CgDODAα1, PgDODAα1 vs McDODAα2, PmDODAα2, CgDODAα2 (Portulacineae and Aizoaceae). Residue numbering is according to Bean et al. (2018). (b) Ancestral sequence reconstructions of codons by empirical Bayesian inference on a maximum likelihood phylogeny of a reduced DODA α sequence alignment. Logo plots at tips give the proportional representation of a given amino acid across all sequences in each collapsed clade for each of the sites identified by Bean et al. (2018). Numbers at nodes match the ancestor of the high‐activity paralogues summarised in (a).
