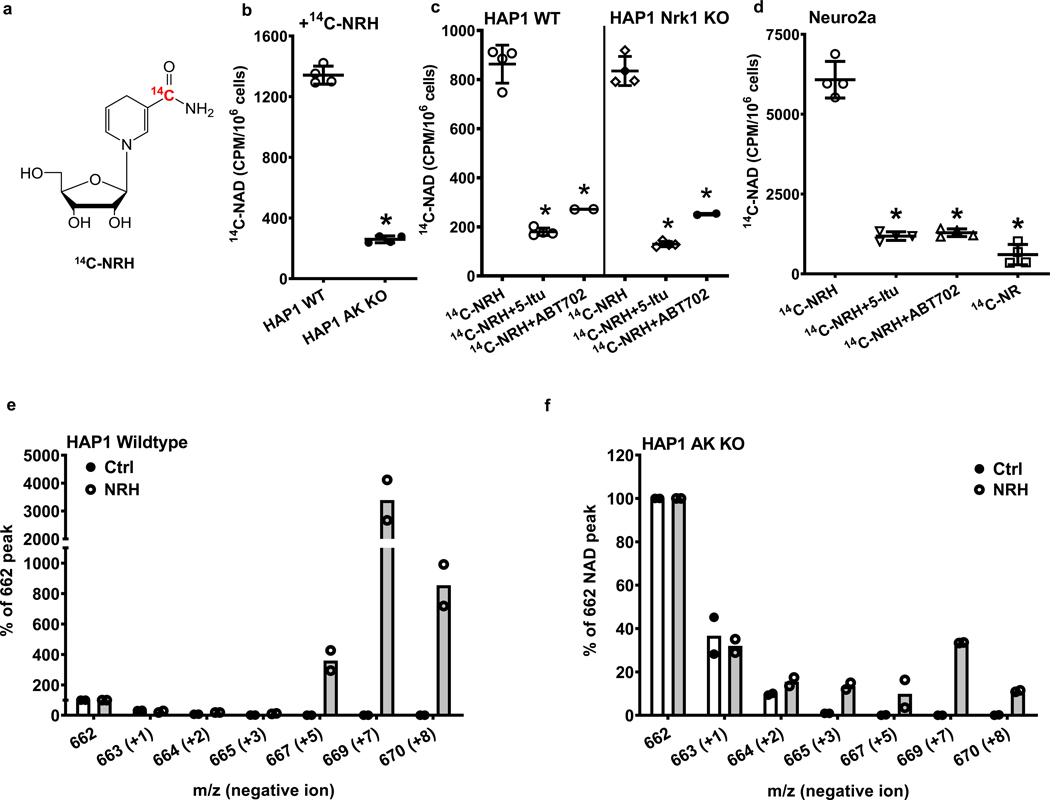
Figure 6.
NRH is incorporated into NAD+ dependent upon AK activity a) Chemical structure of [carbonyl-14C]NRH. b) Radioactivity incorporation from 150 μM [carbonyl-14C]NRH into [carbonyl-14C]NAD+ is significantly abolished in HAP1 AK KO cells comparing to wildtype HAP1 cells. Data expressed as mean ± SD, n=4 biologically independent samples. *, p<0.0001 when compared to WT. c) HAP1 WT and Nrk1 KO cells were treated with 150 μM [carbonyl-14C]-NRH with or without the presence of 26 nM 5-Itu or 20 nM ABT702. Radioactivity incorporations into [carbonyl-14C]NAD+ are shown. Data expressed as mean ± SD, n=2 or 4 biologically independent samples. *, p<0.0001 when compared to 14C-NRH treatment within cell type. d) Radioactivity incorporation from 150 μM [carbonyl-14C]NRH into [carbonyl-14C]NAD in Neuro2a cells is inhibited by treatments with AK inhibitors, 26 nM 5-Itu or 20 nM ABT702. [carbonyl-14C]NR was also treated with matching radioactivity, concentration and incubation time. Data expressed as mean ± SD, n=4 biologically independent samples. *, p<0.0001 when compared to [carbonyl-14C]-NRH treatment. For b) c) d), one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used for statistical analysis. e) HAP1 WT and f) HAP1 AK KO cell treated with vehicle or [carbonyl-18O, U-ribosyl-13C]NRH (300 μM) for 7 hr and the isolated NAD+ analyzed by LCMS. Intensities for different observed peaks with different masses (negative ion mode) are displayed. Endogenous NAD+ not containing isotopes has m/z = 662. [carbonyl-18O, U-ribosyl-13C]NAD+ is peak with m/z = 669. n=2 biologically independent samples.