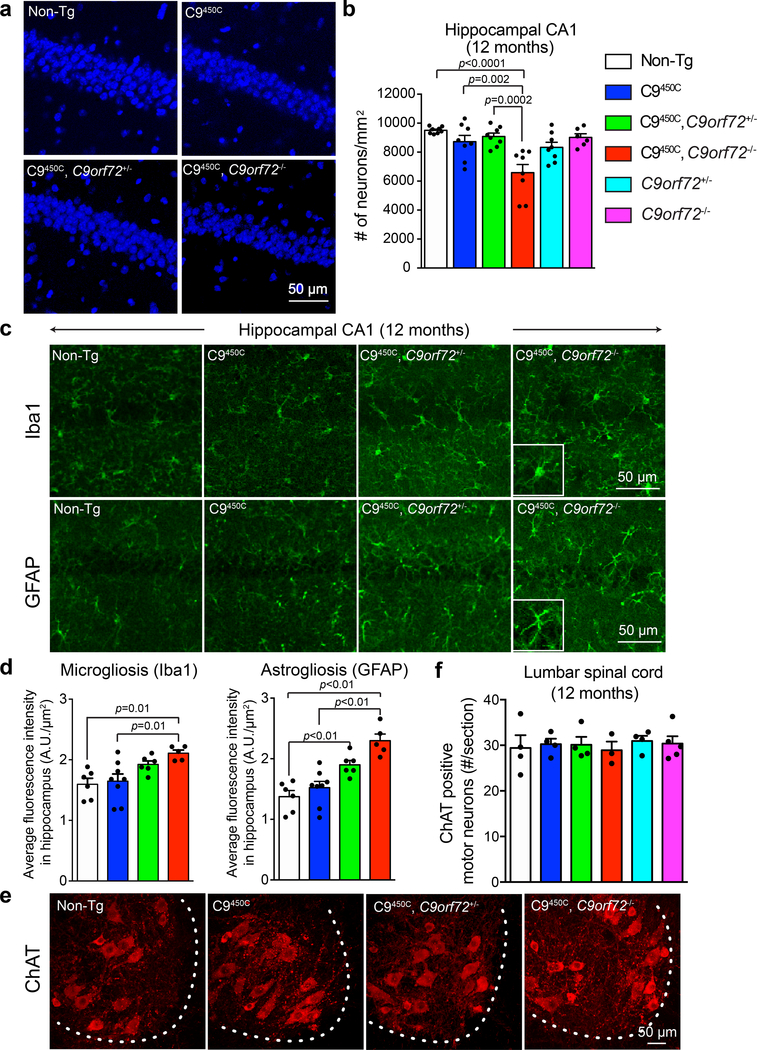
Figure 4: Loss of C9ORF72 promotes degeneration of hippocampal neurons and glial activation in C9450C transgenic mice.
(a-b) Representative images (a) and quantification (b) of DAPI-positive nuclei in the hippocampal CA1 region in 12-month-old C9orf72 transgenic mice with reduced or loss of endogenous C9ORF72. Each solid dot represents a CA1 region from one hemisphere (n = 4 Non-Tg, n = 4 C9450C, n = 4 C9450C,C9orf72+/−, n = 4 C9450C,C9orf72−/−, n = 4 C9orf72+/−, n = 3 C9orf72−/−). Error bars represent SEM. Statistical evaluations were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
(c-d) Representative images (c) and quantification (d) of immunofluorescence staining with antibodies recognizing the microglial marker Iba-1 (upper panels) and the astrocytic marker GFAP (lower panels) in the hippocampal region of 12-month-old C9orf72 transgenic mice with normal, reduced, or absence of endogenous C9ORF72. Each solid dot represents a hippocampal region from one hemisphere per animal (n = 3 Non-Tg, n = 4 C9450C, n = 3 C9450C,C9orf72+/−, n = 3 C9450C,C9orf72−/−). Error bars represent SEM. Statistical evaluations were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
(e) Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive motor neurons detected by immunofluorescence in the anterior horn of lumbar spinal cords of C9ORF72 transgenic mice with reduced or loss of endogenous C9ORF72 at 12 months of age.
(f) Average number of ChAT-positive motor neurons per section from lumbar spinal cords at 12 months of age. Error bars represent SEM (n = 4–5 animals per group). Statistical evaluations were performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.