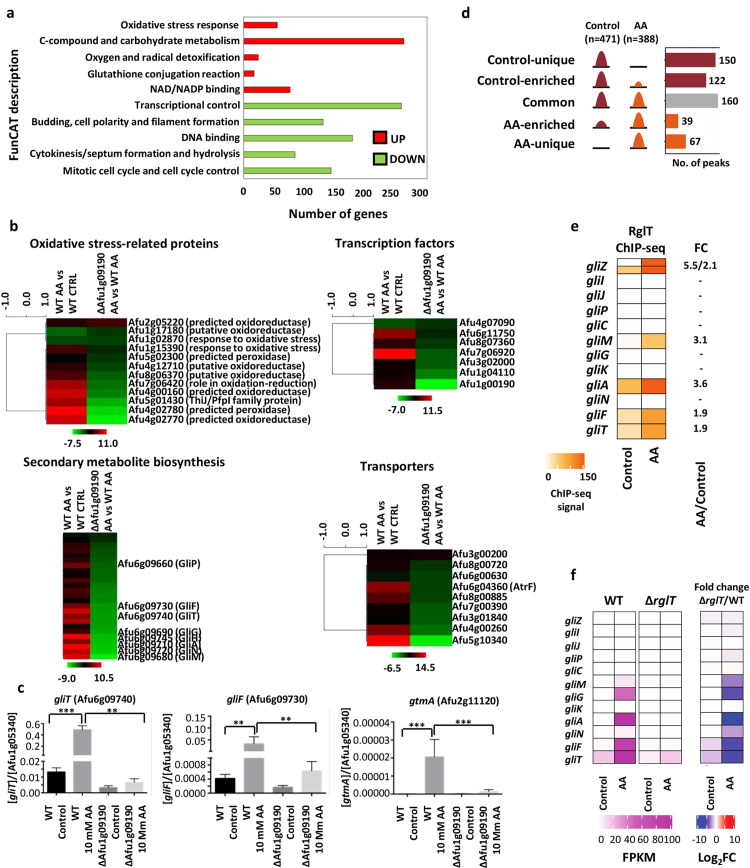
Fig 2. The Afu1g09190-encoded TF regulates the transcription of gliotoxin (GT) biosynthetic genes and of gtmA through directly binding to the promoter regions in the presence of allyl alcohol (AA).
a, AA induces transcriptional up-regulation of genes required for the oxidative stress response whilst down-regulating genes encoding proteins involved in growth in the A. fumigatus wild-type (WT) strain. Functional categorisation (FunCat) description of the 5 most significant enriched categories (p-value < 0.0005), that contain up- (UP) or down (DOWN)-regulated genes with a -1 > Log2 fold-change > 1 (p-value < 0.05), as identified by RNA-sequencing. The WT strain was exposed to 10 mM AA for 30 min after 24 h growth in glucose minimal medium (GMM, control) and gene expression was compared between both conditions. b, Fumagillin and GT biosynthetic genes are severely repressed in the ΔAfu1g09190 strain. Heatmap of the Log2FC values, as determined by RNA-sequencing, of genes that were significantly (p-value < 0.05) differently (-1 > Log2FC < 1) expressed between the WT and ΔrglT in the presence of 10 mM AA for 30 min. Genes were classified into virulence-relevant categories, such as oxidative stress-related proteins, transcription factors, secondary metabolite biosynthesis and transporters. Log2FC gene expression values are also shown for the WT strain, when comparing gene expression in the presence of AA to the control condition. Hierarchical clustering was performed in MeV (http://mev.tm4.org/), using Pearson correlation with complete linkage clustering. c, Validation of the RNA-sequencing data by RT-qPCR. RNA was extracted from strains grown for 24 h in GMM (control) before 10 mM AA was added for 30 min and RT-qPCR was performed. Gene expression values were normalized by gene Afu1g05340, whose expression remained constant across all conditions, as confirmed by RNA-seq. Standard deviations represent three biological replicates (**P-value < 0.001; ***P-value < 0.0001 in a one-way ANOVA test). d, Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled to DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) of the WT and Afu1g09190::HA strains, when grown for 24 h in GMM (control) and then exposed to 10 mM AA for 30 min, identified 538 RglT::HA binding peaks that could be classified into three main groups: i) unique (150) or enriched binding (122) in the control condition, ii) consistent binding (160) in both the control and AA conditions and iii) unique (67) or enriched (39) binding in the AA condition. e, Afu1g09190 binds to the promoter regions of gliZ, gliM, gliA, gliF and gliT and was subsequently named RglT (regulator of GT). Heat map depicting ChIP-seq signal for all genes of the GT biosynthetic gene cluster in the control and AA conditions. Also shown is the differential binding analysis fold change (FC) between both conditions. f, RNA-seq results are in agreement with the ChIP-seq results, confirming that GT biosynthetic genes are under the direct transcriptional control of RglT. Heat maps depicting RNA-seq FPKM values for the WT and ΔrglT strains as well as Log2FC (fold change) values between the WT to the ΔrglT strain of all gli genes in the control and AA conditions.