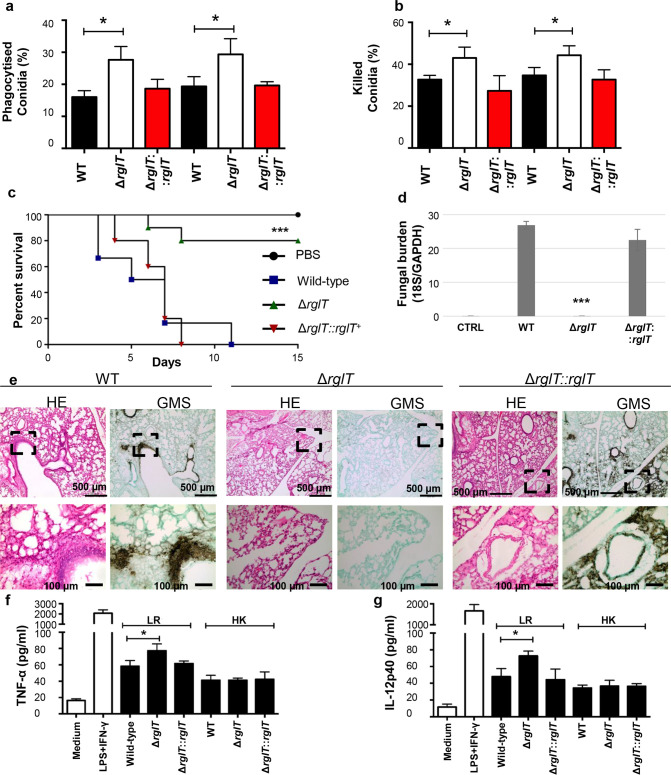
Fig 4. RglT is essential for A. fumigatus virulence.
a, b Bone marrow-derived murine C57BL/6 (wild-type) and CGD (chronic granulomatous disease) macrophages phagocytize (a) and kill (b) a significant higher number of ΔrglT conidia in vitro than when compared to the wild-type (WT) and ΔrglT::rglT strains. Standard deviations represent three biological replicates (*P-value < 0.05 in a two-tailed, unpaired student t-test). c, Survival curve of chemotherapeutic BALB/c mice, which were immunosuppressed with a combination of cyclophosphamide and hydrocortisone, infected intra-nasally with the WT, ΔrglT and ΔrglT::rglT strains show that the ΔrglT strain is hypovirulent (***p-value < 0.0001 in the Mantel-Cox and Gehan-Brestow-Wilcoxon tests, comparing the ΔrglT to the WT and ΔrglT::rglT strains). d, Fungal burden of the naïve control (CTRL = phosphate buffered saline), WT, ΔrglT and ΔrglT::rglT strains show a significant (***p-value < 0.0001 in a two-tailed, unpaired student t-test) reduction of the ΔrglT growth in chemotherapeutic murine lung tissue at 3 days post-infection. e, Histopathology of murine lungs at three days post-infection with the WT, ΔrglT and ΔrglT::rglT strains indicates the absence of ΔrglT proliferation in the lung tissue. 5 μm lung tissue sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (HE) or with Grocott’s Methenamine Silver (GMS) before slides were viewed and pictures taken. f, Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and g, interleukin (IL)-12p40 concentrations in macrophages infected with heat killed (HK) conidia or live-resting (LR) conidia.