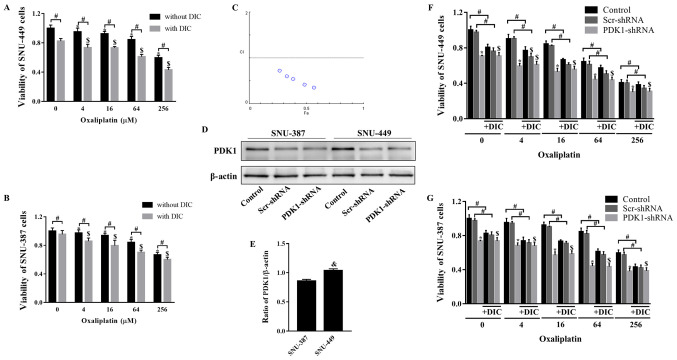
Figure 2.
DIC and OXA synergistically inhibit tumor growth in vitro. (A) SNU-449 cells and (B) SNU-387 cells were treated with OXA (4, 16, 64, or 256 µM) for 24 h with or without DIC (25 µM) and cell viability was assayed by MTT assay. *,$P<0.05 vs. control; #P<0.05 DIC treatment vs. no DIC treatment at the same concentration of OXA. (C) The combination index (CI) of DIC and OXA obtained from the growth inhibitory experiments, additive effect (CI=1), synergism (CI <1) and antagonism (CI >1) in drug combinations. (D) SNU-387 and SNU-449 cells were transiently transfected for 48 h with the shPDK1 expression vector or empty vector, and western blot analysis was performed to examine the levels of PDK1. (E) Quantified results of PDK1 in SNU-387 and SNU-449 cells. &P<0.05 SNU-449 vs. SNU-387 cells. (F) SNU-449 cells and (G) SNU-387 cells were treated with OXA (4, 16, 64 or 256 µM) for 24 h with or without DIC (25 µM) and treated as described in (D), and cell viability was assayed by MTT assay. *,$P<0.05 vs. control. #P<0.05 DIC treatment vs. no DIC treatment at the same concentration of OXA. Data are presented as the means ± SE from 3 independent experiments. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PDK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; DIC, dicoumarol; OXA, oxaliplatin.