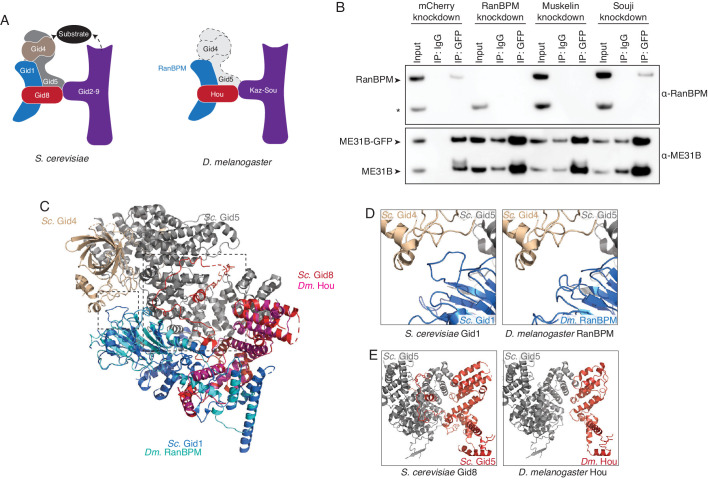
Figure 5. The Drosophila CTLH complex has a different organization than the S. cerevisiae Gid complex.
(A) Schematic of the S. cerevisiae Gid complex based on recent cryo-EM structures (Qiao et al., 2020), and the Drosophila CTLH complex, based on orthology of the subunits. (B) The interaction between ME31B-GFP and RanBPM depends on Muskelin, but not Souji. ME31B-GFP complexes were immunoprecipitated from 1 to 2 hr embryo lysates using α-GFP or IgG (as a control). Immunoprecipitations were performed in 1–2 hr embryo lysates with mCherry, RanBPM, Muskelin, or Souji knocked-down. Membranes were probed with α-GFP or α-RanBPM. * indicates a non-specific band. (C) RanBPM and Hou share general structural similarities with their yeast orthologs. RanBPM (teal) and Hou (magenta) were threaded through structures of their orthologs, Gid1 (blue) and Gid8 (red), respectively. (D) RanBPM lacks the Gid4-interacting loop. Shown is the region of the S. cerevisiae Gid complex (left) and D. melanogaster CTLH complex (right) where Gid1 interacts with Gid4. The corresponding loop is missing in RanBPM. (E) Houki lacks the Gid5-interacting tail. Shown is the region of the S. cerevisiae Gid complex (left) and D. melanogaster CTLH complex (right) where Gid8 interacts with Gid5. The corresponding tail is missing in Houki. For simplicity, only Gid5 and Gid8 are shown.