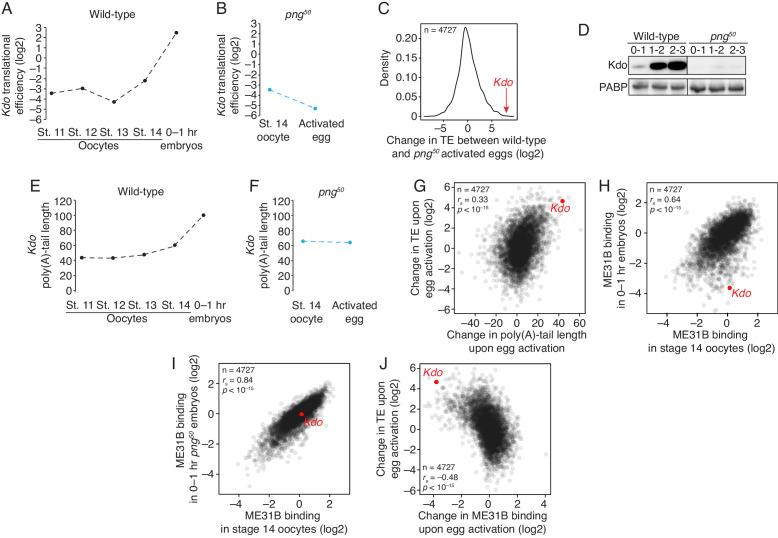
Figure 7. The PNG kinase mediates translational upregulation of Kdo at egg activation.
(A) Translation of Kdo increases at egg activation. Translational efficiency of Kdo mRNA was measured in published ribosome profiling datasets (Eichhorn et al., 2016). Shown is the translational efficiency in stage 11, 12, 13, and 14 oocytes, and 0–1 hr embryos. (B) Translational upregulation of Kdo depends on PNG. As in A, except for png50 stage 14 oocytes and activated eggs. (C) Translation of Kdo is highly dependent on PNG. Shown is a density plot of the difference in translational efficiency between wild-type and png50 embryos. The difference in translational efficiency for Kdo mRNA is shown by an arrow. (D) Production of Kdo during embryogenesis depends on PNG. Staged wild-type or png50 embryos were harvested at the indicated times after egg laying. Western blotting was performed on the lysates, probing for Kdo and PABP (as a loading control). (E) Kdo mRNA poly(A)-tail length increases at egg activation. As in A, except plotting poly(A)-tail lengths from Eichhorn, et al. (F) Lengthening of Kdo mRNA poly(A)-tail length depends on PNG. As in B, except plotting poly(A)-tail length. (G) Changes in poly(A)-tail length during egg activation correlate with changes in translation efficiency. Shown is scatter plot comparing, for each gene, the change in poly(A)-tail length between stage 14 oocytes and 0–1 hr embryos and the change in its translational efficiency. Kdo is highlighted in red. (H) ME31B changes upon egg activation. Shown is a scatter plot comparing ME31B binding to mRNAs in stage 14 oocytes and 0–1 hr embryos. Kdo is highlighted in red. (I) Changes in ME31B binding upon egg activation depend on PNG. As in H, except comparing ME31B binding in stage 14 oocytes and 0–1 hr png50 embryos. (J) Changes in ME31B at egg activation correlate with changes in translational efficiency. Shown is a scatter plot comparing changes in ME31B binding between stage 14 oocytes and 0–1 hr embryos and changes in translational efficiency. Kdo is highlighted in red.
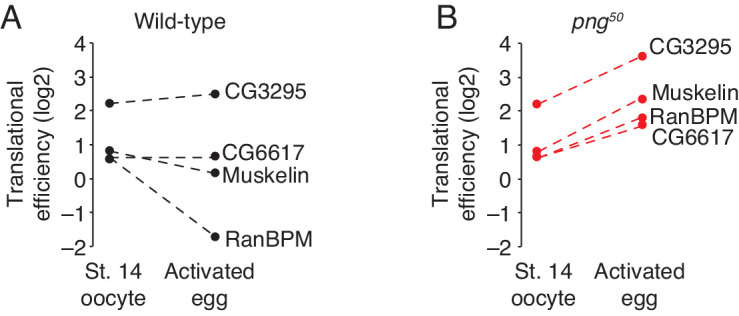
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Translation of CTLH components does not increase during the oocyte-to-embryo transition.