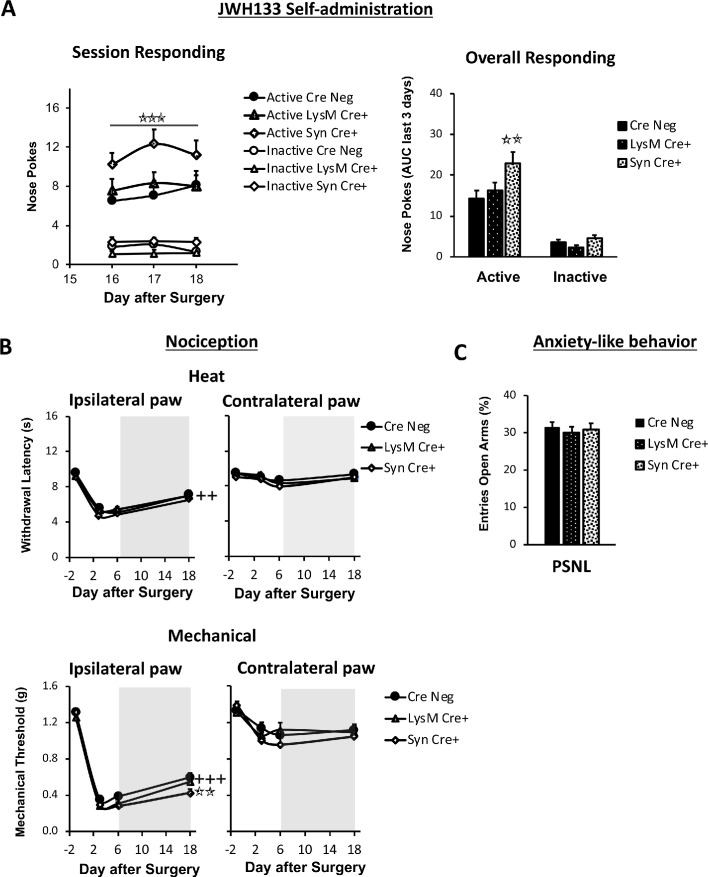
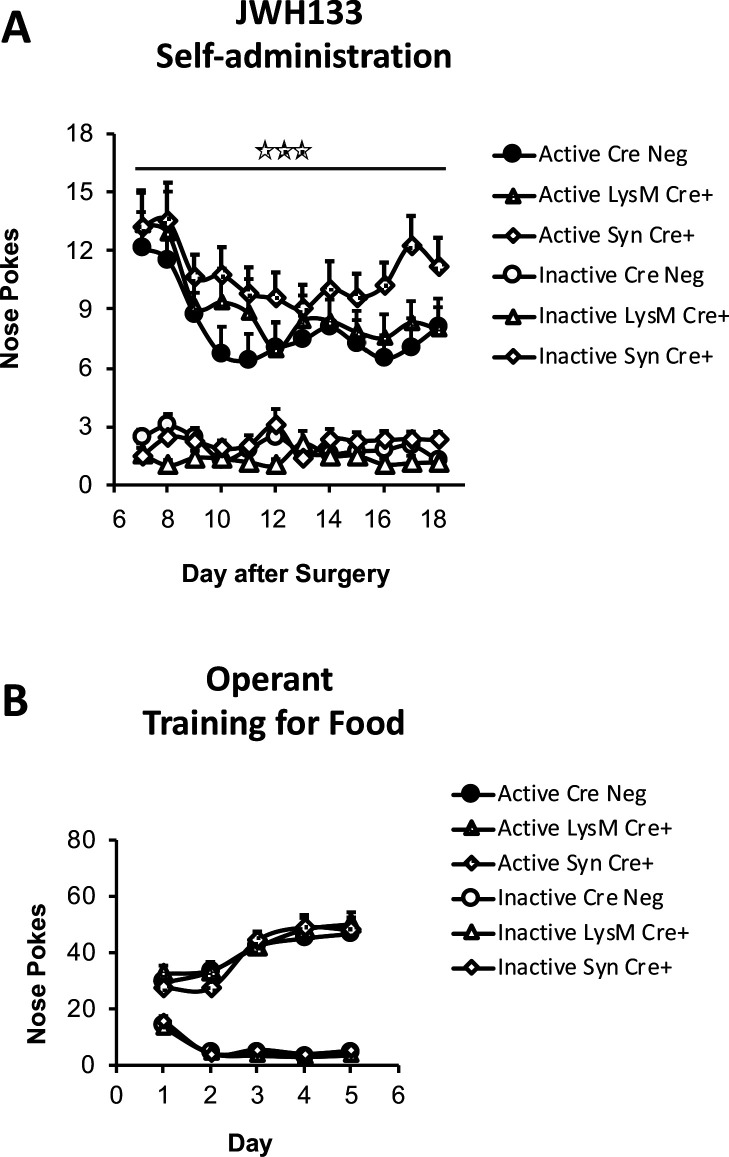
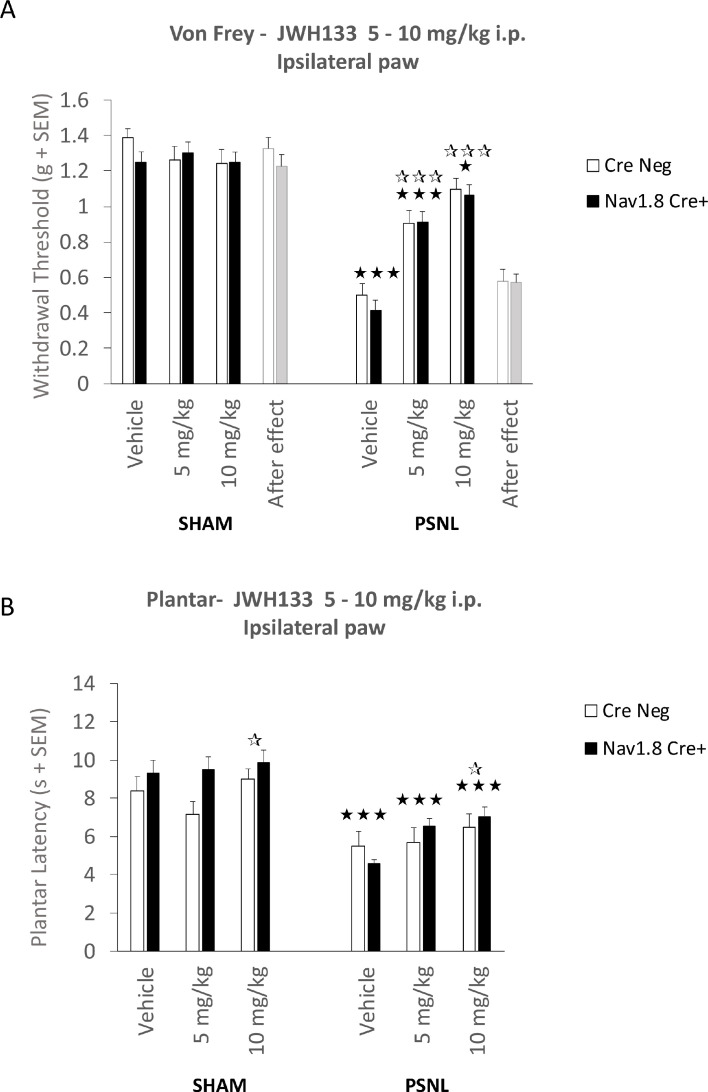
Figure 3. Nerve-injured mice defective in neuronal CB2 receptor show increased self-administration of the CB2 agonist JWH133 and a decrease in the antinociceptive effects of the drug.
Mice lacking CB2 in neurons (Syn-Cre+), in monocytes (LysM-Cre+) or their wild-type littermates (Cre Neg) were food-trained in Skinner boxes (Food training, 5 days), subjected to partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL, day 0), catheterized and exposed to JWH133 (0.3 mg/kg/inf., days 7 to 18). Nociceptive sensitivity to heat (Plantar) and mechanical (von Frey) stimulation were measured before and after nerve injury (−1,3,6,18), anxiety-like behavior was evaluated at the end (day 19). (A) Syn-Cre+ mice showed increased active operant responding for JWH133 in the last sessions of the self-administration period (B) All mouse strains showed decreased heat nociception after JWH133 treatment, and Syn-Cre+ mice showed reduced effects of JWH133 on mechanical nociception. (C) Every mouse strain showed similar anxiety-like behavior after JWH133 self-administration. No significant differences were found between LysM-Cre+ and Cre Neg mice. N = 18–36 mice per group. Mean and error bars representing SEM are shown. Shaded areas represent drug self-administration. Stars represent comparisons vs. Cre Neg mice; crosses represent day effect. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.