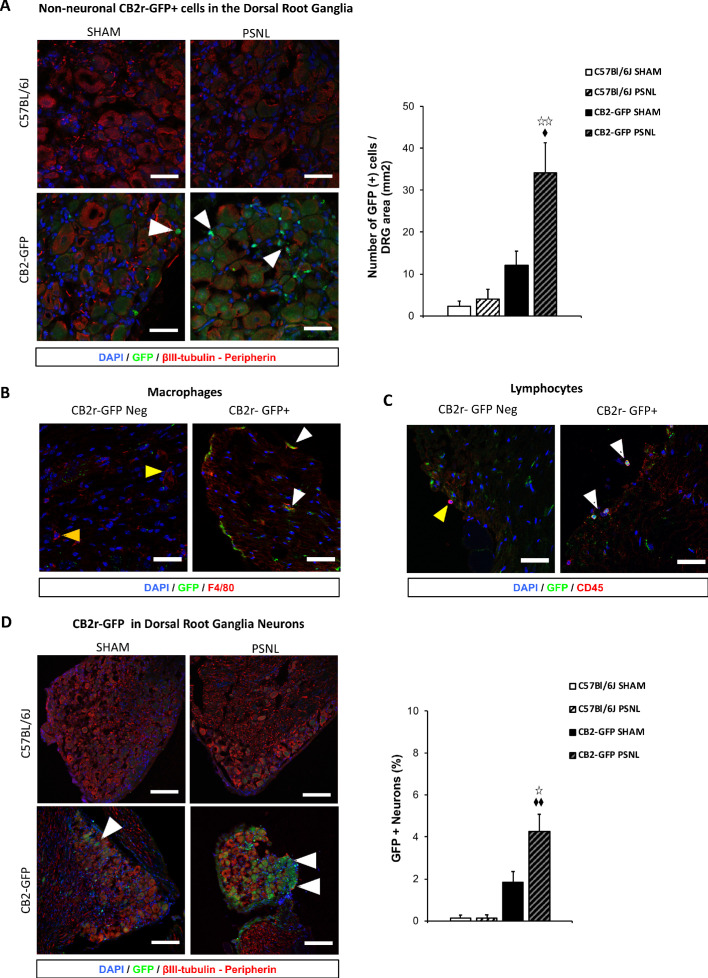
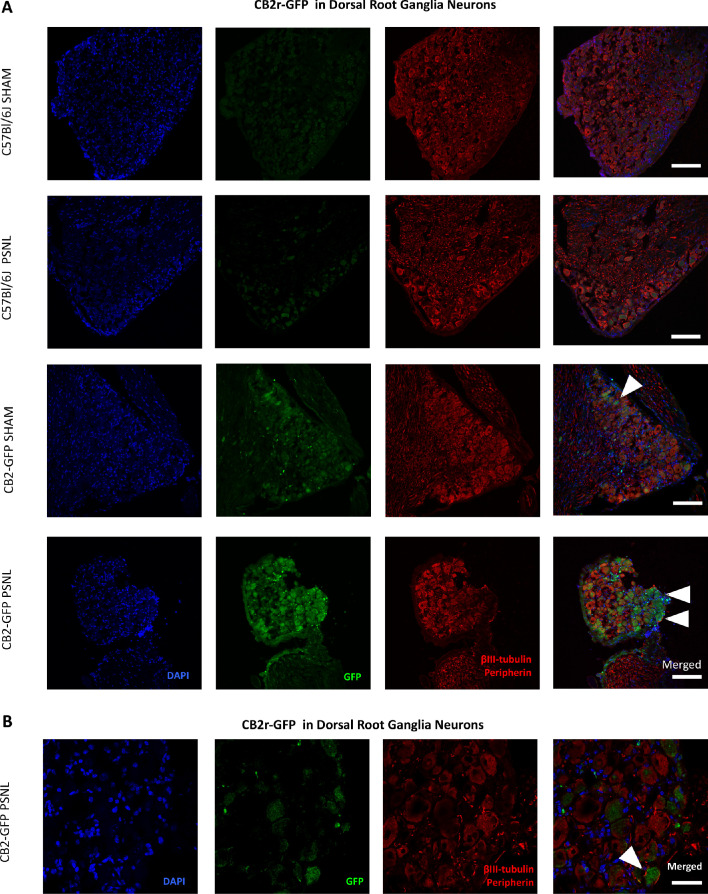
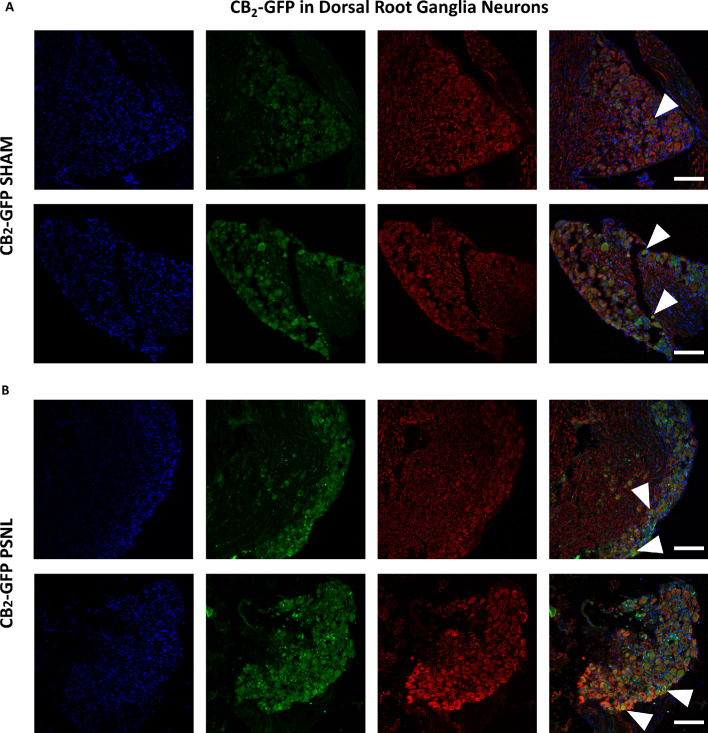
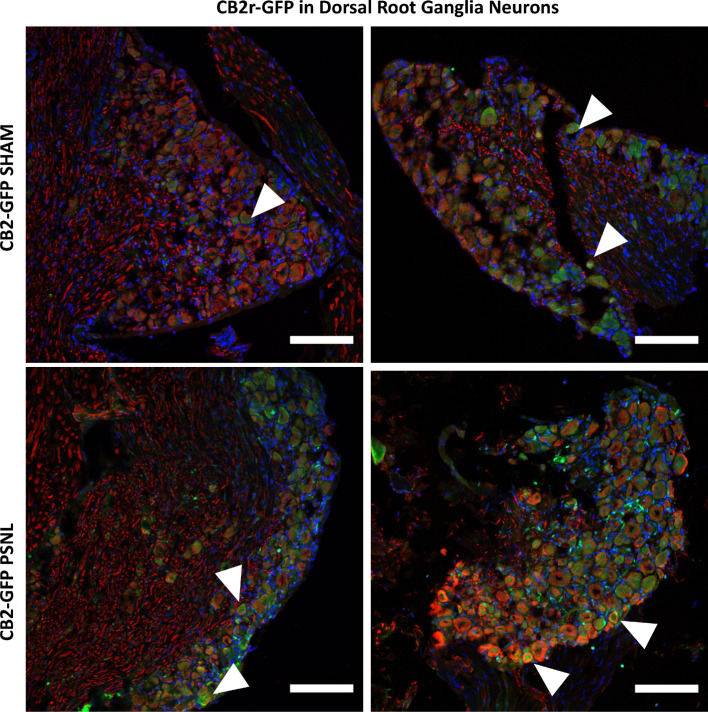
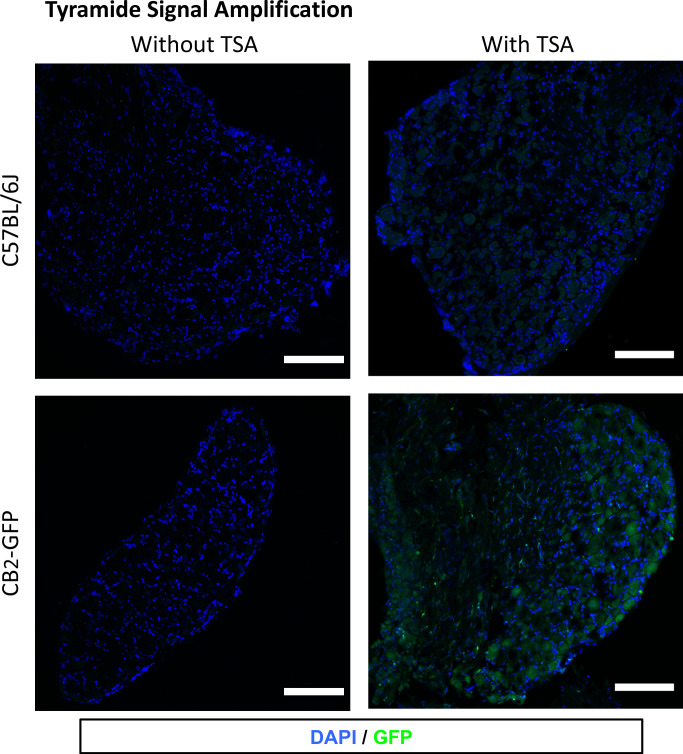
Figure 4. CB2 receptor-GFP immune cells infiltrate the dorsal root ganglia of the injured nerve and GFP from bone-marrow-derived cells is also found inside peripheral neurons.
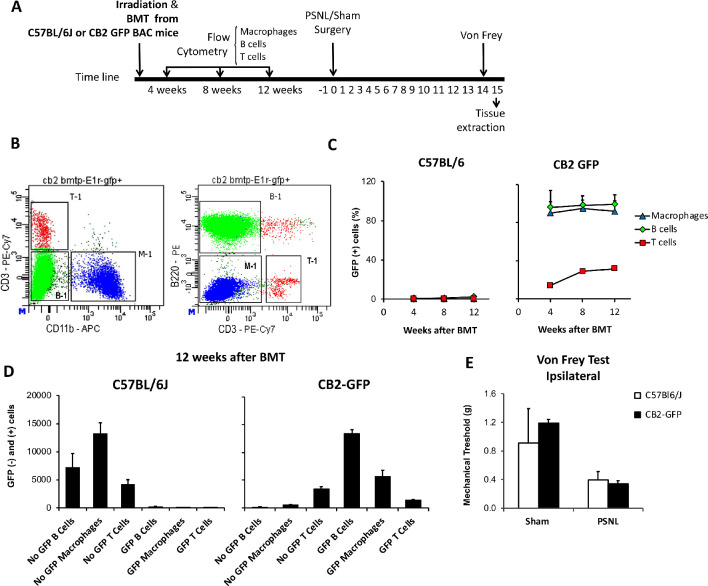
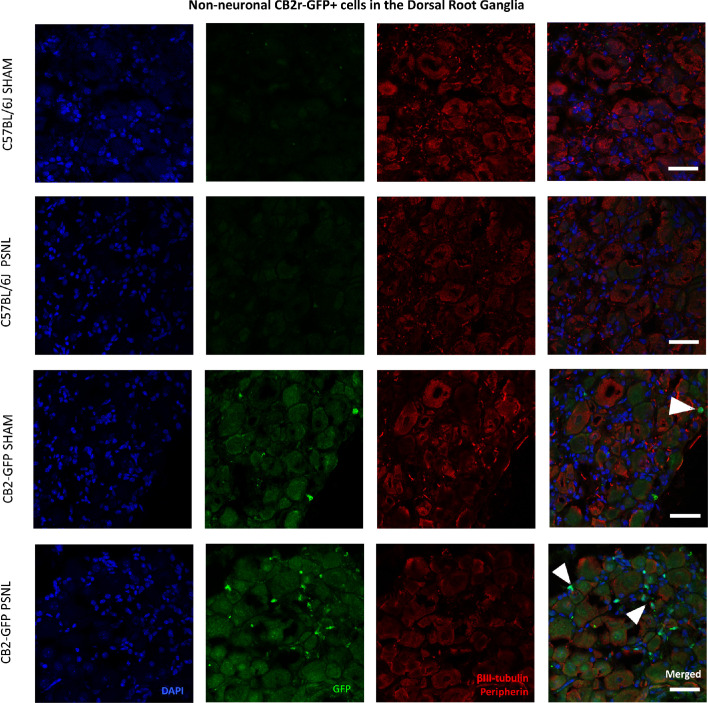
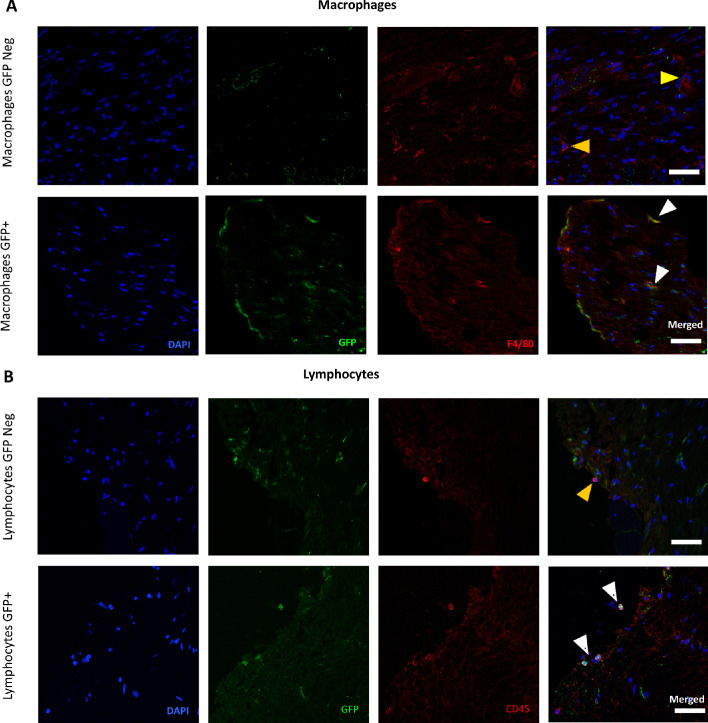
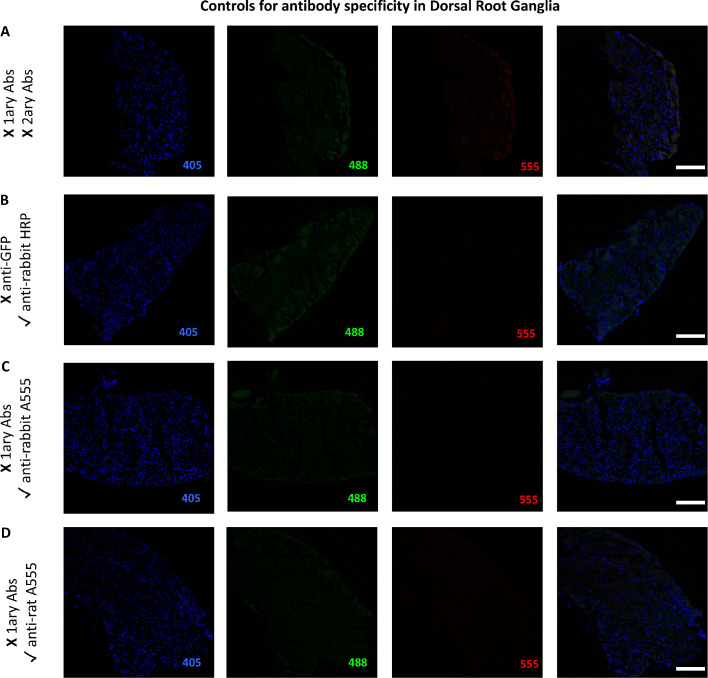
The figure shows images of L3-L5 dorsal root ganglia from sham (SHAM) or nerve-injured mice (PSNL) transplanted with bone marrow cells from CB2 GFP BAC mice (CB2-GFP) or C57BL6/J mice (C57BL6/J). (A, D) Dorsal root ganglia sections stained with the nuclear marker DAPI (Blue), anti-GFP (Green), and neuronal markers anti-β-III tubulin and anti-peripherin (Red). (A) CB2-GFP mice showed significant infiltration of GFP+ bone-marrow-derived cells after the nerve injury, whereas sham or nerve-injured C57BL6/J mice did not show significant GFP immunorreactivity. Split channels in Figure 4—figure supplement 2. (B) Co-localization of CB2-GFP and the macrophage marker anti-F4/80. Co-staining with anti-GFP and anti-F4/80 revealed GFP+ (~60%) and GFP negative macrophages infiltrating the injured nerve. Split channels in Figure 4—figure supplement 3A. (C) Co-staining with anti-GFP and anti-CD45 revealed GFP+ (~40%) and GFP-negative lymphocytes infiltrating the injured nerve. Split channels in Figure 4—figure supplement 3B. (D) CB2-GFP mice showed a percentage of GFP+ neurons that was enhanced with the nerve injury. Scale bar, 140 μm. Split channels in Figure 4—figure supplement 4. Scale bar for B), C), D), 45 μm. Yellow arrows point to GFP negative cells and white arrows to GFP+ cells. A certain degree of image processing has been applied equally across the entire merged images for optimal visualization. N = 2–3 mice per group. Means and error bars representing SEM are shown. Stars represent comparisons vs. sham; diamonds vs. C57BL6/J. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Flow cytometry of blood from CB2-GFP and C57BL6/J mice in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Additional images of Sham and nerve-injured CB2-GFP mice in Figure 4—figure supplements 5 and 6. Specificity tests for Tyramide Signal Amplification in Figure 4—figure supplement 7. Controls for antibody specificity in Figure 4—figure supplement 8.