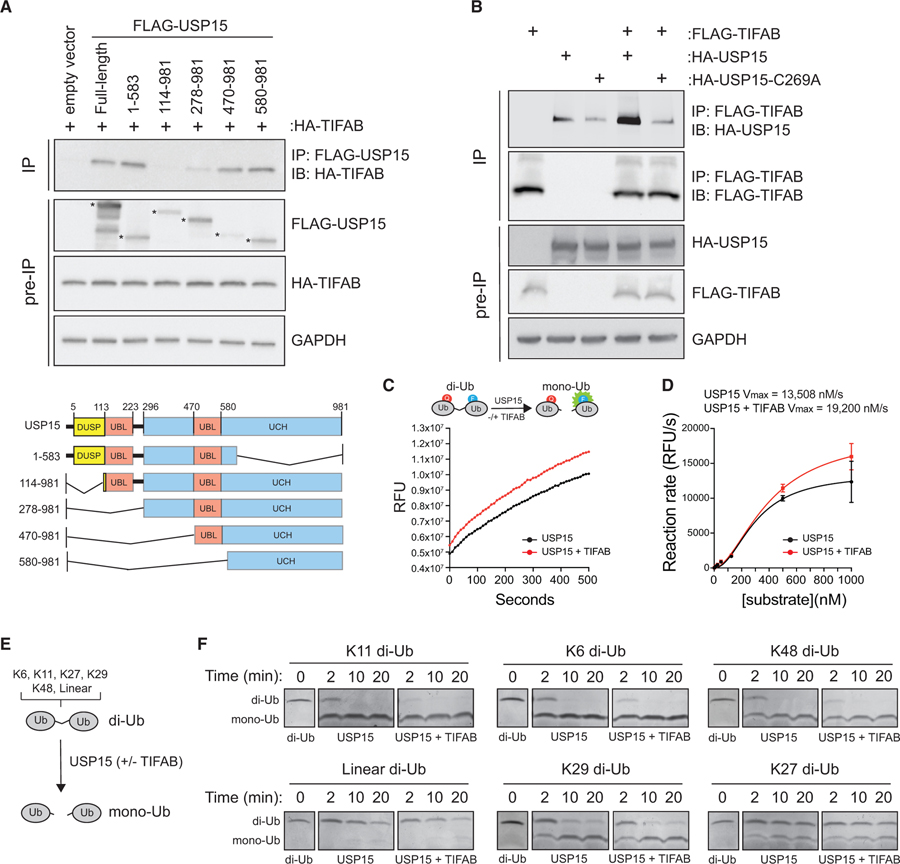
Figure 2. TIFAB Binds the Catalytic Domain of USP15 and Increases Its Rate of Deubiquitination.
(A) Top: immunoblotting of HA-TIFAB on lysates immunoprecipitated for FLAG-USP15 deletion mutants that were isolated from HEK293T cells transfected with HA-TIFAB and the indicated FLAG-USP15 mutants. Bottom: schematic of human USP15 with key functional domains. DUSP, domain present in ubiquitin-specific peptidases; UBL, ubiquitin-like domain; UCH, ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase.
(B) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-TIFAB and immunoblotting for wild-type or catalytically inactive USP15 (C269A) from HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG-TIFAB alone, HA-USP15 constructs alone, and FLAG-TIFAB combined with HA-USP15 constructs (lanes 4 and 5).
(C) Cell-free deubiquitination assay utilizing internally quenched fluorescent (IQF) diubiquitin as a substrate for USP15. 500 nM K48-linked diubiquitins was incubated with 50 nM USP15 plus mock buffer (black) or USP15 plus 50 nM recombinant TIFAB (red). Relative fluorescent units (RFUs) measured over time by spectrometry are a readout of USP15 activity. Four replicates were analyzed per group for two independent experimental assays.
(D) The reaction rate (RFU/s) of the linear phase of the reaction (~500 s) plotted as a function of diubiquitin substrate concentration using an allosteric sigmoidal model to calculate Vmax. Increasing amounts of diubiquitins were added to the reaction with 50 nM USP15 and 50 nM TIFAB until the rate of ubiquitin hydrolysis by USP15 began to saturate. The USP15 rate of reaction is increased by adding TIFAB to the reaction (red versus black). Four replicates were analyzed per group for two independent experimental assays.
(E) Schematic of the orthogonal deubiquitination assay.
(F) Coomassie-stained gels containing diubiquitin incubated with USP15 alone or USP15 with TIFAB for the indicated times. Diubiquitins for which USP15 has a high affinity (K11, K6, and K48) are in the top row (USP15 dependent). Diubiquitins for which USP15 has low affinity (K29, linear, and K27) are in the bottom row (USP15 independent). Panels were constructed by assembling images from the respective sections of gels containing the proteins indicated.