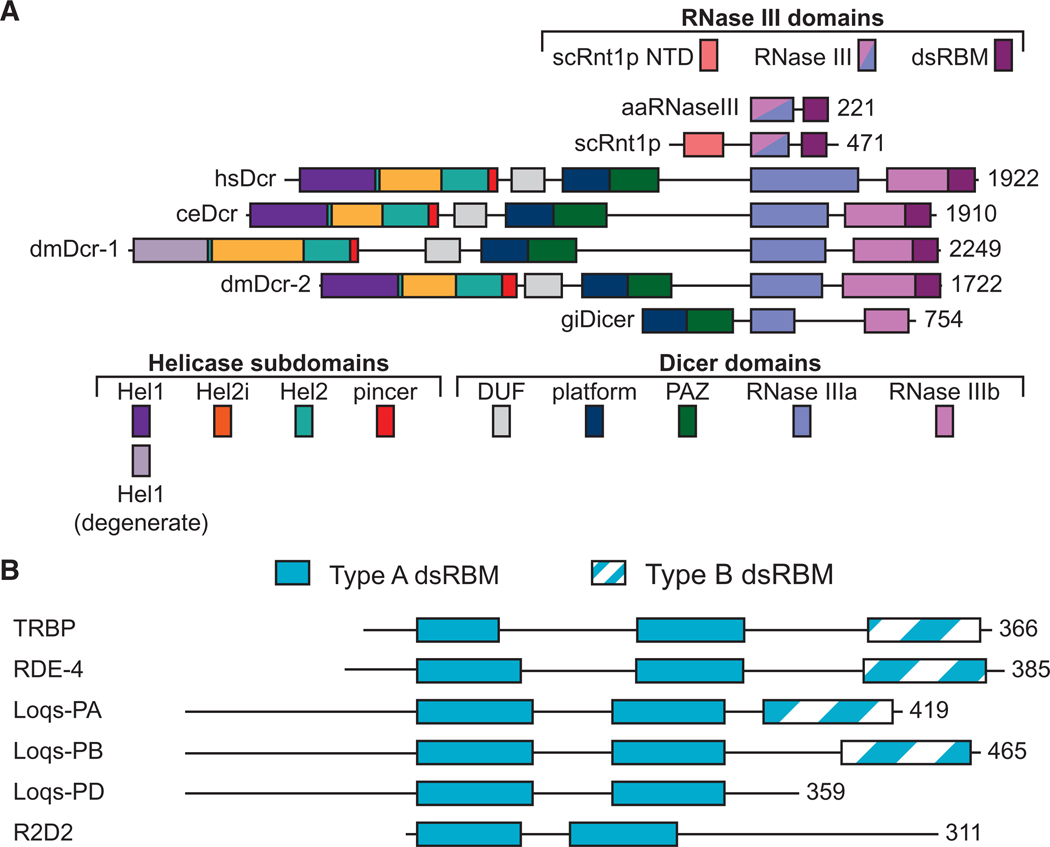
Figure 1.
(A) Domains of Dicer and RNase III open-reading frames including Aquifex aeolicus RNase III (aaRNaseIII), Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rnt1p (scRnt1p), Homo sapiens Dicer (hsDcr), Caenorhabditis elegans Dicer (ceDcr), Drosophila melanogaster Dicers (dmDcr-1 and dmDcr-2), and Giardia intestinalis Dicer (giDicer). Domains are to scale and anchored at the amino terminus of aaRNase III, with the carboxy-terminal amino acid numbered on the right. (Top) color coding of RNase III domains, including amino-terminal domain (NTD). (Bottom) Color coding of helicase subdomains and Dicer domains. (B) Domain organization of Dicer-interacting dsRBPs noting Type A (solid) and Type B (striped) double-stranded RNA binding motifs (dsRBMs). Open-reading frames are to scale and anchored by the amino terminus of the first dsRBM. Numbers at the far right indicate the carboxy-terminal amino acid.