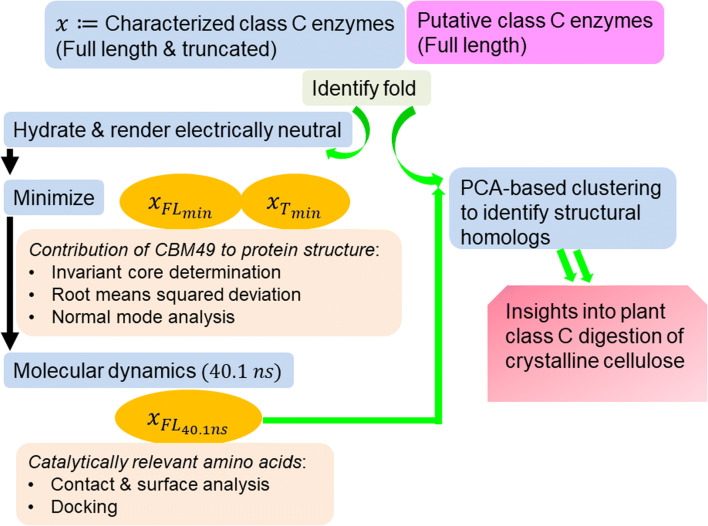
Fig. 1.
Schema for biophysical characterization of class C GH9 enzymes. Generic protocol to assess contribution of GH9, CBM49, and the linker to catalysis of crystalline cellulose by plant class C enzymes. These steps consisted of fold identification, 3D protein and ligand geometry optimization, invariant core determination and normal mode analysis, surface analysis, cavity and groove delineation, and docking. Folds of characterised (full length, truncated) class C enzymes and putative class C sequences were initially identified. 3D models of class C enzymes with the top scoring templates (non-plant) were used for all further analysis; energy minimization (Emin) of the 3D models was used to compare the effects of truncation on the structural integrity of the protein. Equilibrium structures (40.1 ns) were used subsequently to delineate the active site architecture of plant class C GH9 endoglucanases as well as conduct detailed docking studies with cellulose based ligands. Abbreviations—GH, glycoside hydrolase; CBM, carbohydrate binding module; Phyre2, protein homology/analogy recognition engine