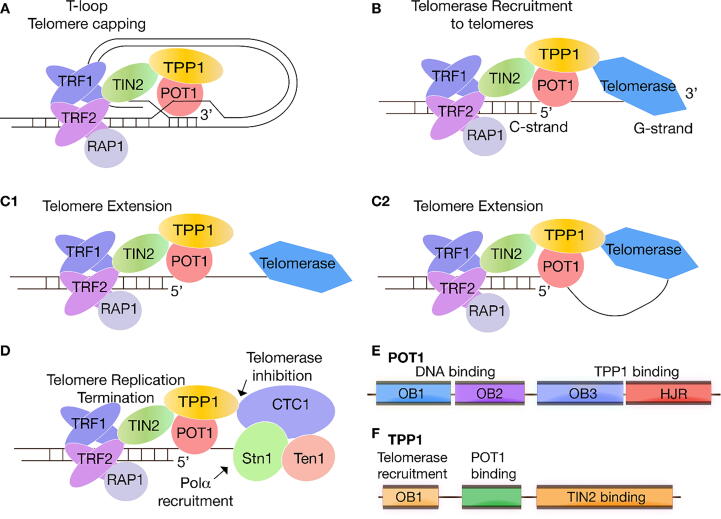
Fig. 1.
Schematic of shelterin and CST activities at telomeres. A. Shelterin facilitates T-loop formation at the ends of our chromosomes. B. Telomerase is recruited by the POT1-TPP1 processivity factor. C1 and C2. Two possible mechanisms of telomerase-dependent telomere extension: telomerase may have a transient interaction with TPP1 (C1) or remain tethered to TPP1 during telomere replication (C2). D. Inhibition of telomerase dependent telomere replication by the CST complex. E. POT1 contains three OB folds (OB1, OB2, OB3) and one Holliday Junction Resolvase (HJR) domain. While the N-terminal OB1 and OB2 bind ssDNA, OB3 and the HJR domain bind TPP1. F. TPP1 contains an N-terminal OB-fold involved in telomerase recruitment to telomeres, and a POT1- and TIN2-binding domains.