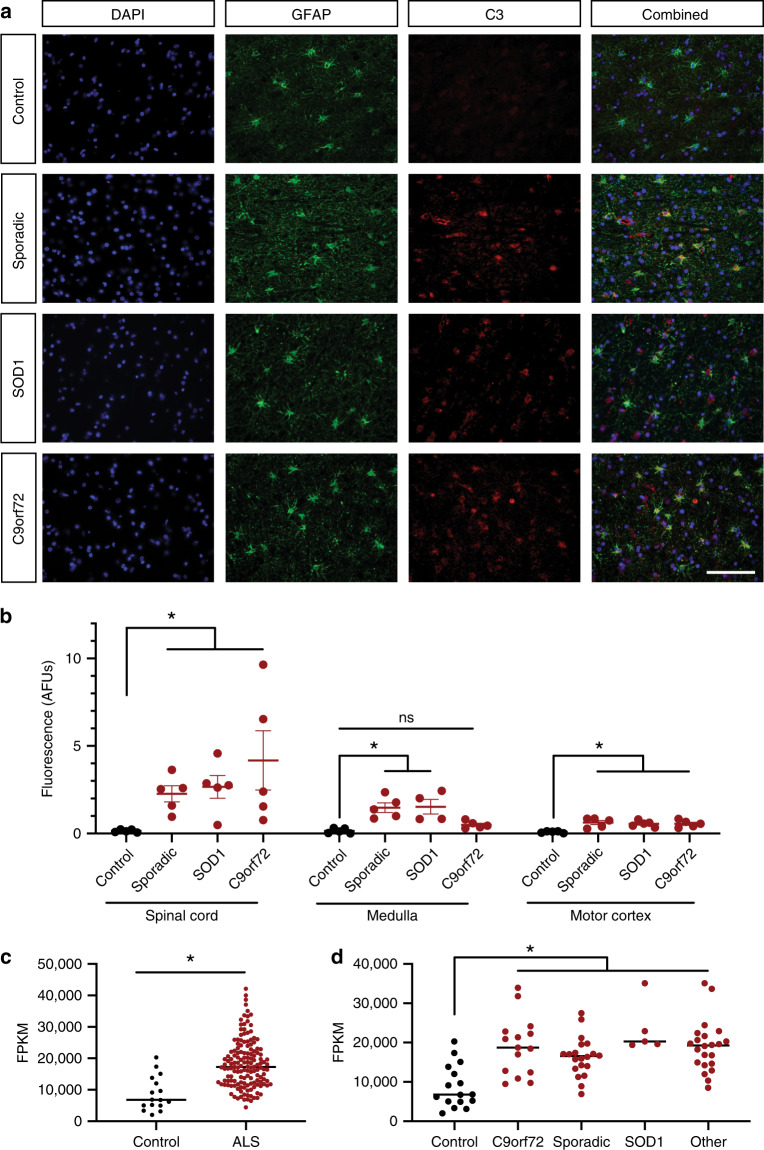
Fig. 3. Neuroinflammatory astrogliosis is a common pathology in human ALS.
a Example images of cortical samples from patients with sporadic, SOD1, and C9orf72 associated ALS as well as nonneurological controls stained with DAPI for nuclei, GFAP for astrocytes, and C3 as a marker for neuroinflammatory astrocyte activation. (quantified in b; scale bar = 100 µm) b Quantification of C3 immunoreactivity within GFAP+ astrocytes in the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex. There was significantly more C3 staining within astrocytes in all subtypes of ALS compared to controls in the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex except for samples of the medulla from C9orf72 associated ALS patients. (*p < 0.05 by Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric test corrected for multiple comparisons using the Dunn method; mean ± s.e.m.) c Bulk RNA-seq C3 expression from the spinal cord of ALS patients vs control (*p < 0.05 by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test; mean). d Subsampling of data in c by identified ALS subtype (other = other genetic cause; *p < 0.05; two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test, corrected by Dunnett method; mean).