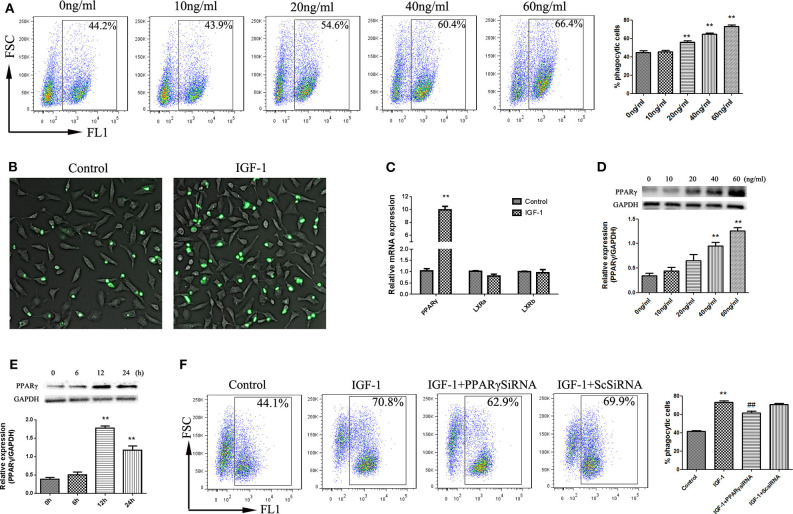
Figure 9.
IGF-1 promotes apoptotic cell phagocytosis by AECs through PPARγ. (A,B) AECs (1 ×105 cells/well) were inoculated into a 6-well plate, stimulated with different concentrations of IGF-1 (0, 10, 20, 40, and 60 ng/mL) for 12 h, and co-cultured with FITC-labeled apoptotic cells for a total of 4 h. Phagocytosis of apoptotic cells was detected by flow cytometry (A) and fluorescence microscopy (B). **P < 0.01 vs. the 0 ng/mL group. (C) AECs (1 ×106 cells/well) were inoculated into a 6-well plate, stimulated with IGF-1 (60 ng/mL) for 24 h, and qRT-PCR was used to detect PPARγ, LxRA, and LxRB mRNA expression in AECs. **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. (D) AECs (1 ×105 cells/well) were inoculated into a 6-well plate and treated with IGF-1 at different concentrations (0, 10, 20, 40, and 60 ng/mL) for 24 h. The protein expression of PPARγ was detected by western blotting. **P < 0.01 vs. the 0 ng/ml group. (E) AECs were stimulated with IGF-1 (60 ng/mL) for 6, 12, and 24 h, and the protein expression of PPARγ in AECs was detected by western blotting. **P < 0.01 vs. the 0 h group. (F) AECs (1 ×105 cells/well) were inoculated into a 6-well plate, transfected with PPARγ siRNA or scrambled (Sc) siRNA for 36 h, and stimulated with IGF-1 (60 ng/mL) for 12 h. FITC-labeled apoptotic cells were added to the culture for 4 h. AEC phagocytosis of apoptotic cells was detected by flow cytometry. **P < 0.01 vs. the control group, ##P < 0.01 vs. the IGF-1 group.