FIGURE 3.
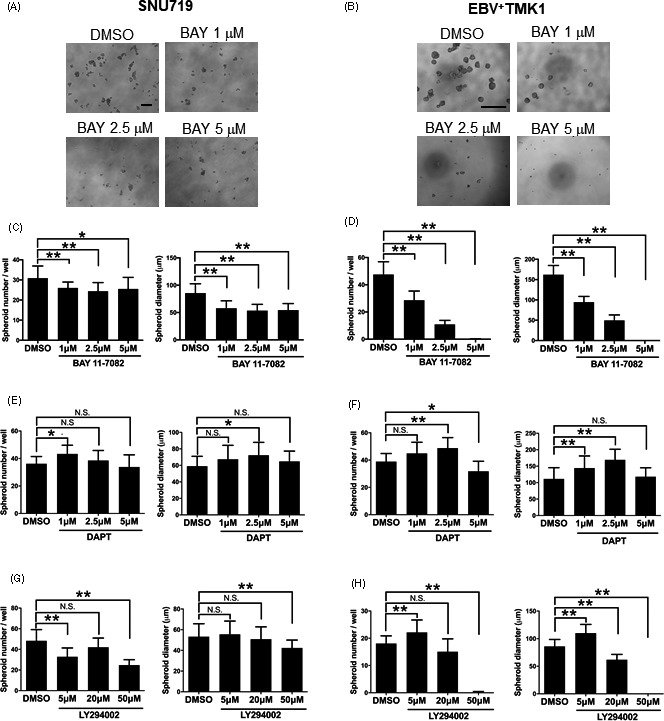
Nuclear factor‐κB (NF‐κB) pathway contributes to maintenance of cancer stem cells in Epstein‐Barr virus (EBV)‐associated gastric cancer. A, Spheroid formation assay of SNU719 cells treated with the NF‐κB inhibitor, BAY 11‐7082 (1, 2.5, or 5µmol/L). A total of 10000 cells were seeded in each well. Measurement of the number (left graph) and diameter (right graph) of spheroid colonies after 7days. B, Spheroid formation assay of EBV+ TMK1 cells treated with the NF‐κB inhibitor, BAY 11‐7082 (1, 2.5, or 5µmol/L). A total of 500 cells were seeded in each well. Measurement of the number (left graph) and diameter (right graph) of spheroid colonies after 7days. C, E, Spheroid formation assay in SNU719 cells treated with the Notch inhibitor (γ secretase inhibitor IX, DAPT) (1, 2.5, or 5µmol/L) (C) or PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (5, 20, or 50µmol/L) (E). A total of 10000 cells were seeded in each well. Measurement of the number (left) and diameter (right) of spheroid colonies after 7days. D, F, Spheroid formation assay of EBV+ TMK1 cells treated with Notch inhibitor (γ secretase inhibitor IX, DAPT) (1, 2.5, or 5µmol/L) (D) or PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (5, 20, or 50µmol/L) (F). A total of 500 cells were seeded in each well. Measurement of the number (left) and diameter (right) of spheroid colonies after 7days. All data are shown as mean±SD; *P<.05, **P<.01, Dunnett’s test. N.S., not statistically significant
