Fig. 3. T. cruzi infection has a persistent, spatially heterogeneous impact on the microbiota.
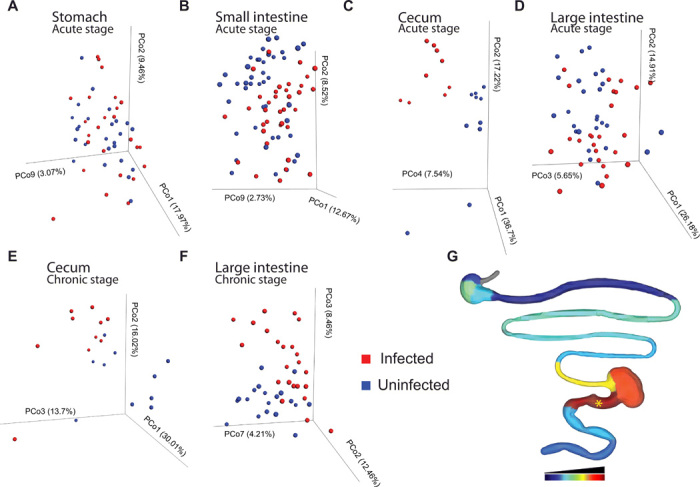
Representation of between-sample differences in microbial community composition through principal coordinate transformation of unweighted UniFrac distances. (A to D) Comparison of acute-stage infected and uninfected samples from stomach (A), small intestine (B), cecum (C), and large intestine (D). (E and F) Comparison of cecum (E) and large intestine (F) samples from uninfected and persistently infected mice. Spatial heterogeneity was also observed within an organ (G), with the highest disturbances in the microbiota in the proximal large intestine (sampling position 11). (G) R2 at each sampling site in the acute stage [logarithmic scale, scaled from lowest R2 (dark blue) to highest R2 (dark red)]. *PERMANOVA P < 0.05.
