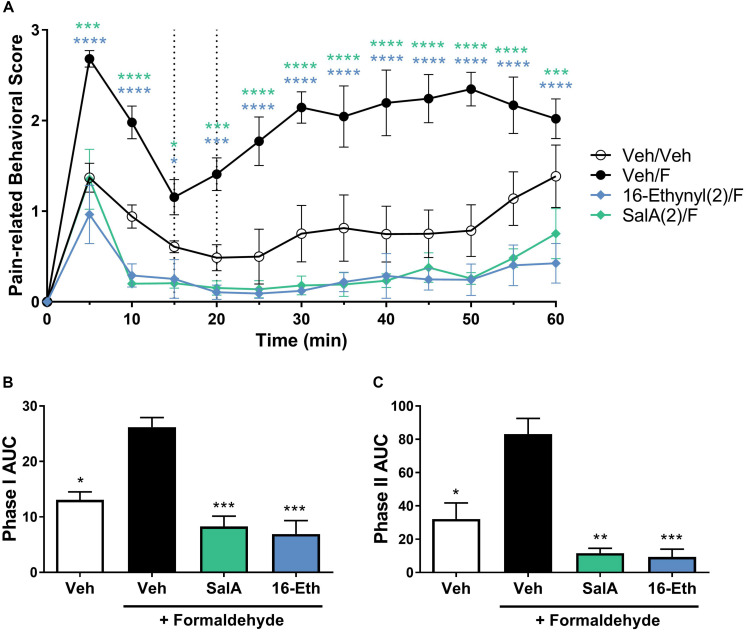
FIGURE 5.
Local adminstration of 16-Ethynyl SalA produced antinocieptive effects in the intraplantar 2% formaldehyde assay. (A) Time course of pain-related behavior following intraplantar 2% formaldehyde injection into the right hind paw. 16-Ethynyl SalA (2 mg/kg i.pl.) treatment showed a significant reduction in pain-related behavior compared to the vehicle/formaldehyde-treated control. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. (B,C) Area under the curve (AUC) analysis of phase I (B) and II (C) pain-related behaviors. 16-Ethynyl SalA reduced both phases of pain-related behavior. Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s post-tests. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 for 2 mg/kg doses vs. vehicle/formaldehyde control. Values presented as mean ± SEM, n = 6. Number in brackets indicates dose in mg/kg and F = formaldehyde i.pl. administration.