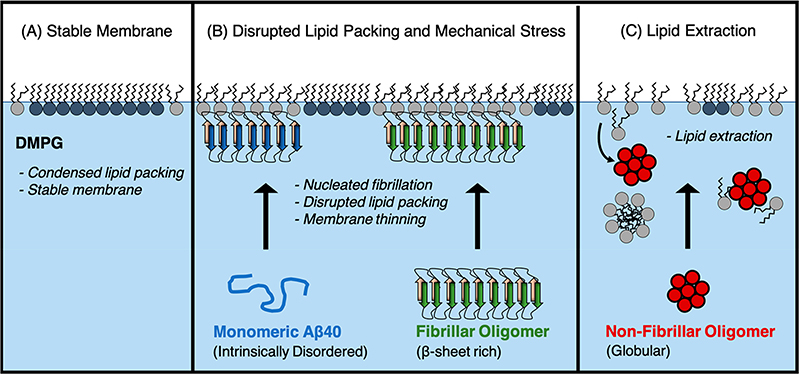
Figure 10.
Model for two mechanisms of membrane-mediated toxicity. (A) The anionic lipid DMPG forms a stable monolayer with many phospholipids packed into condensed domains. (B) Aβ40 monomer binds the membrane and transitions to a β-sheet rich protofibrillar structure. Membrane-bound FOs retain their protofibrillar structure. The observed membrane thinning and disruption to the phospholipid packing likely contribute toward their toxicities. (C) Nonfibrillar oligomer extracts lipids from the membrane, likely resulting in micelles and formation of protein/phospholipid complexes that detach from the membrane.