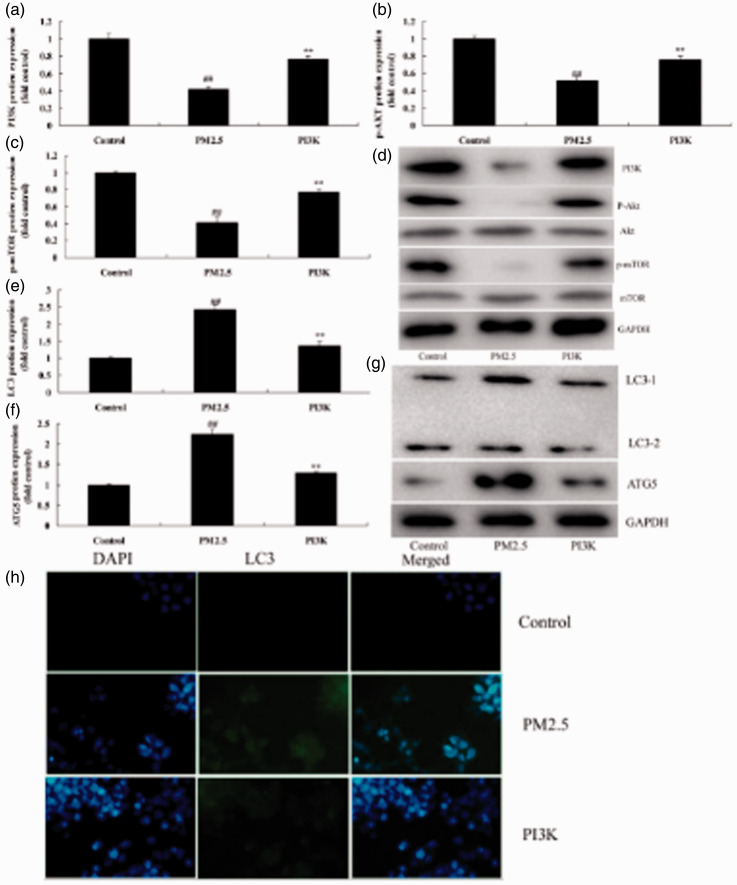
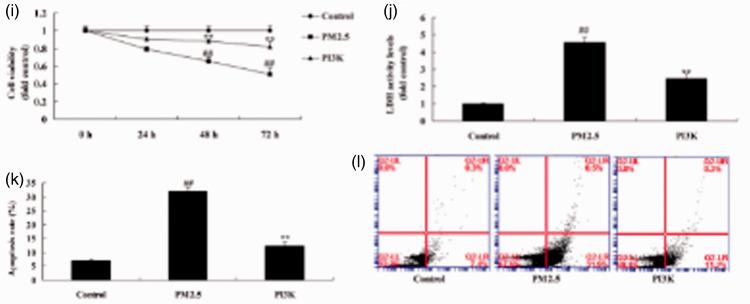
Figure 5.
Activation of PI3K reduced apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells in an in vitro model of COPD induced by PM2.5. Protein expression of PI3K, p-AKT, and p-mTOR by statistical analysis (a, b, and c) and western blotting assays of PI3K, p-AKT, and p-mTOR protein level (d); protein expression of LC3 and ATG5 by statistical analysis (e and f) and western blotting assay of LC3 and ATG5 protein level (g), immunofluorescence for PI3K protein expression (h), cell growth (i), LDH activity (j), and apoptosis rate (k and l). **P < 0.01 compared with negative control group; ##P < 0.01 compared with HBECs cells induced by PM2.5. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; PM2.5, particulate matter with a diameter <2.5 µm; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; Control, negative control group; PM2.5 group, human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) induced by PM2.5; PI3K group, HBECs induced by PM2.5 and treated with PI3K.