Figure 3. Temporospatial Chromatin Looping of the Chr27 β-Keratin Gene Cluster during Skin Development.
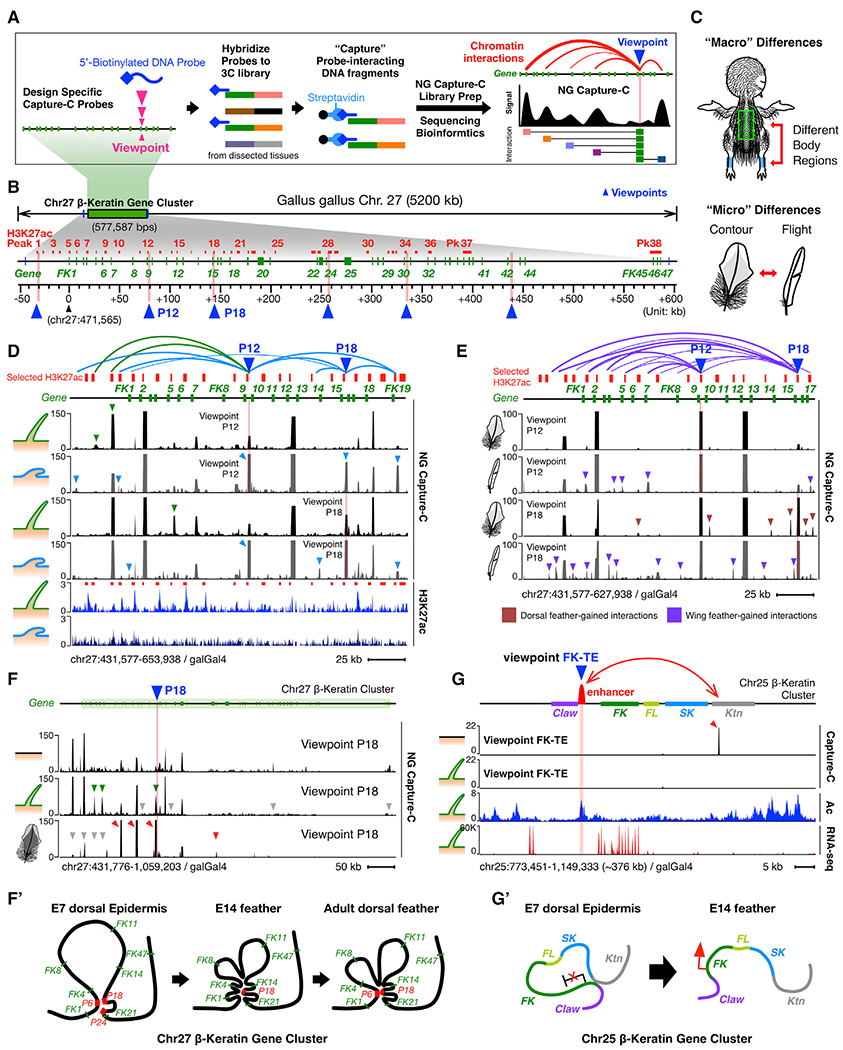
(A) Schematic of NG Capture-C experiment and its data presentation.
(B) Schematic of selected H3K27ac regions as candidate looping anchors at the Chr27 β-krt cluster. Red lines, selected H3K27ac regions; pink bars and blue triangles, bait sites (viewpoints) used in NG Capture-C experiments.
(C) Schematic of experimental design for comparison of skin “macro” and “micro” differences.
(D) NG Capture-C interactions of different skin regions (feather filaments and scale epidermis) from the same-aged chicks (E14).
(E) NG Capture-C interactions of different feather types (dorsal contour feather barbs and flight feather barbs) from the same-aged adult chickens.
(F) NG Capture-C interactions of different aged skins (E7, E14, and adult) from the same dorsal back region. Green triangles, feather-specific chromatin interactions; red triangles, adult contour feather-specific chromatin interactions.
(F′)Schematic of dynamic intra-cluster chromatin looping of Chr27 β-krt cluster during feather-skin development.
(G) NG Capture-C interactions of FK-TE at the Chr25 β-krt cluster.
(G′) Schematic of dynamic and inter-subcluster chromatin looping at the Chr25 β-krt cluster.
