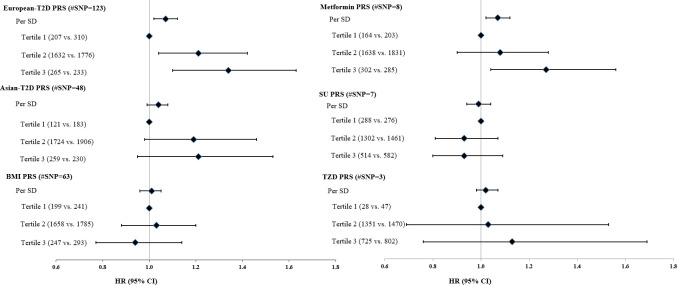
Fig 3. Association between PRSs and progression to requirement of insulin treatment.
HRs were adjusted for all clinical risk factors identified by stepwise variable selection, including age at diagnosis, gender, duration of diabetes, year of diagnosis, smoking status, LDL-C, HbA1c, log triglyceride, log urinary ACR, eGFR, retinopathy, sensory neuropathy, history of chronic kidney disease, and use of different medications (yes/no). Number of progressors versus nonprogressors was presented in parentheses for each subgroup. ACR, albumin-to-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PRS, polygenic risk score; SD, standard deviation; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; SU, sulphonylurea; TZD, thiazolidinediones.