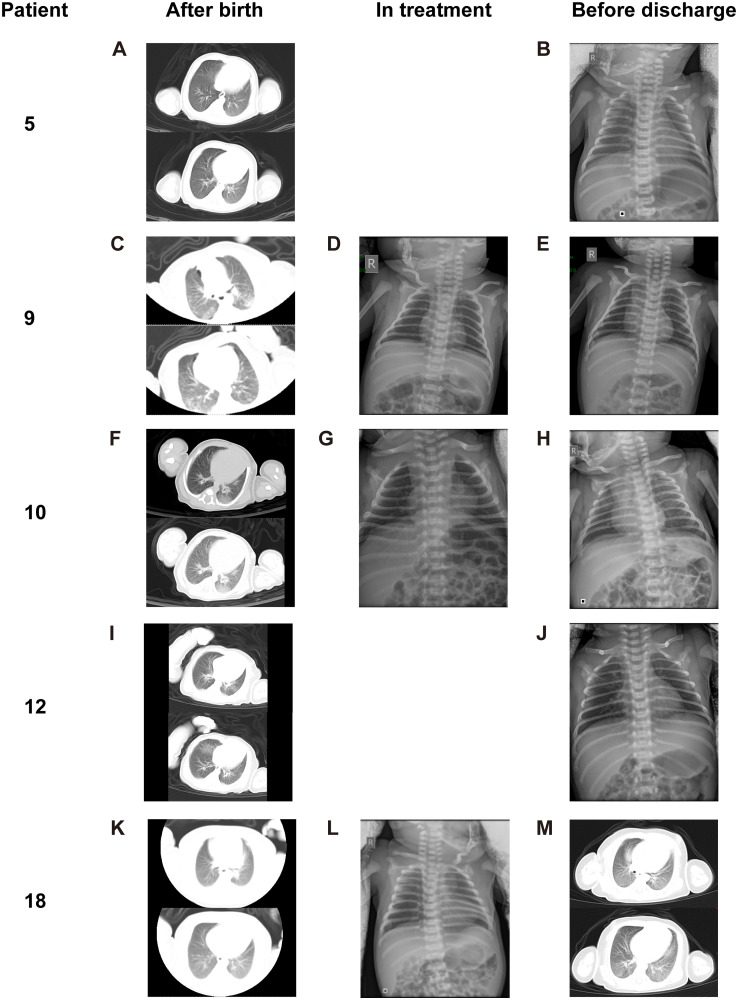
Fig 2. Chest X-ray or CT (transverse plane) images of 5 neonates diagnosed with COVID-19 infection (2 confirmed, 3 suspected) after birth, in the treatment, and before discharge.
(A-B, Patient 5) Chest CT images (A) obtained after birth showed peripheral GGOs in the posterior basal segment of left lung lower lobe. Chest X-ray film (B) before discharge showed no abnormal findings. (C-E, Patient 9) Chest CT images (C) showed diffuse GGO with multifocal consolidations in the peripheral regions of bilateral lungs. Chest X-ray film (D) in treatment showed patchy obscure shadows in bilateral lung lower fields. Chest X-ray film (E) before discharge showed complete disappearance of pneumonia. (F-H, Patient 10) Chest CT images (F) obtained after birth showed patchy GGO in the posterior basal segment of right lower lobe and large GGO in the posterior basal segment of left lower lobe. Chest X-ray film (G) in treatment showed significant release of pneumonia. Chest X-ray film (H) before discharge showed nothing abnormal findings except mild increased lung markings. (I-J, Patient 12) Chest CT images (I) obtained after birth showed peripheral focal consolidations in the posterior basal segments of bilateral lower lobes and multiple patchy GGO bilaterally. Chest X-ray film (J) showed partial absorption of pneumonia. (K-M, Patient 18) Chest CT images (K) obtained after birth showed reduced latency with GGO in bilateral lower lobes. Chest X-ray film (L) in treatment showed increased bilateral lung markings. Chest X-ray film (M) before discharge showed increased densities of previous existing pulmonary lesions with interlobular septal thickening. All images have been de-identified to protect patient privacy. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CT, computed tomography; GGO, ground-glass opacity.