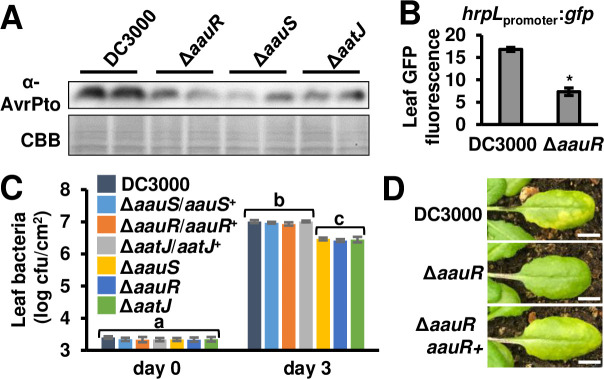
Fig 2. AatJ, AauS and AauR are required for maximal level of DC3000 virulence in Arabidopsis leaves.
(A) AvrPto levels in Arabidopsis leaves syringe-infiltrated with 1 x 108 cfu/mL of DC3000, ΔaauS, ΔaauR, ΔaauSR, or ΔaatJ strains. Upper panel is immunoblot detection of AvrPto in infected leaf tissue collected 6 hours post-infiltration. Lower panel is Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining of blot as a loading control. (B) GFP fluorescence of Arabidopsis leaf tissue syringe-infiltrated with 5 x 108 cfu/mL of DC3000 or ΔaauR hrpLpromoter:gfp reporter strains. Graphed are means ± SE of GFP fluorescence from infected tissue 6 hours post-infection, n = 3. Asterisks denote significant difference between strains based on t-test, P < 0.001. (C) 1 x 106 cfu/mL of DC3000, ΔaauS, ΔaauR, ΔaatJ and respective complemented strains were syringe-infiltrated into Arabidopsis leaves. Leaf bacteria populations were enumerated on day 0 and day 3 by serial dilution plating of leaf extracts. Graphed are log-transformed means ± SE of bacteria colony-forming units (cfus) isolated from infected tissue, n = 6 for day 0 and n = 8 for day 3. Small-case letters denote significance groupings based on ANOVA with Bonferroni correction, P < 0.01. Data shown were pooled from two independent experiments. Results from additional replicated experiments are shown in S3 Fig. (D) Photograph of disease symptoms on leaves 3 days post-syringe infiltration with 1 x 106 cfu/mL of DC3000, ΔaauR or ΔaauR/aauR+. White line is 0.5 cm.