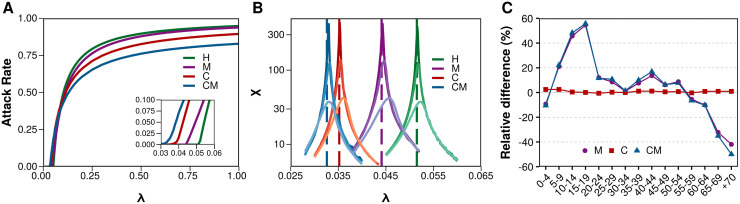
Fig 2. Dynamics of a SIS model using different contact models.
A) The fraction of infected individuals as a function of the infection rate. In the inset, the area near the epidemic threshold for each configuration is shown enlarged. B) Susceptibility as a function of the infection rate for the four configurations with populations of size 104, 105 and 106. The larger the size of the population the closer the peak of susceptibility is to the theoretical epidemic threshold (dashed line). C) Relative difference in the number of infected individuals between the results obtained using the M (purple circles), C (red squares) or CM (blue triangles) models and the homogeneous mixing setting. Positive values indicate that the number of infected individuals is larger than in the homogeneous mixing scenario, while negative values represent a lower number of infected individuals.