Figure 3. Allocation of nitrogen for NEAAs synthesis.
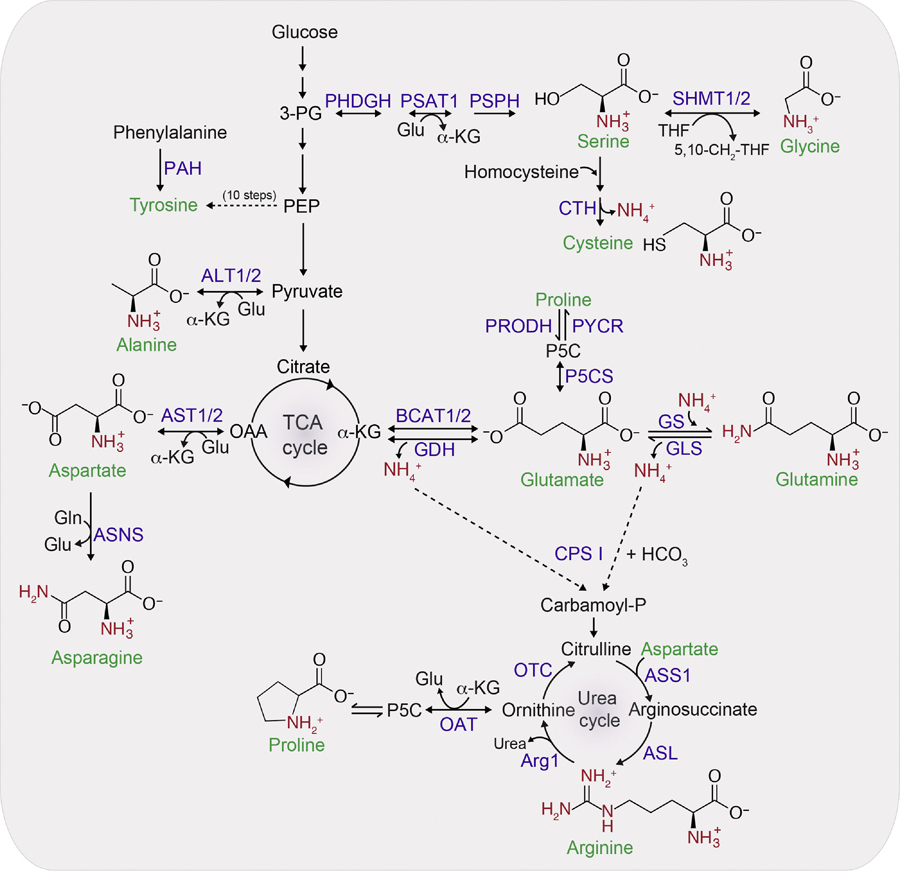
Glutamine provides the nitrogen for asparagine synthesis and glutamate provides the nitrogen for all other NEAAs synthesis. The carbon backbone for the synthesis of serine, glycine and cysteine comes from 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PG). Glycine can be directly generated from serine via the reversible reaction catalyzed by SHMT1/2 enzyme. One carbon (1C) units from the serine is transferred to the carrier molecule tetrahydrofolate (THF) resulting in 5,10-CH2-THF. Since this reaction is reversible, the directionality depends upon the supply and demand of 1C units. For the synthesis of cysteine from serine, the sulfur atom comes from methionine in the form of homocysteine. Cystathionase (CTH) catalyzes the removal of nitrogen as a free ammonium ion from homocysteine. Tyrosine is usually synthesized in one step from phenylalanine, but in conditions where phenylalanine is limiting, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) serves as a carbon backbone for tyrosine and is synthesized in 10 steps. Alanine, which is the second-most abundant amino acid in plasma after glutamine, can be synthesized from pyruvate by ALT1/2. Majority of the intracellular aspartate is generated from oxaloacetate by the enzyme aspartate aminotransefases (AST1/2 or GOT1/2). Asparagine is synthesized from aspartate and is the only amino acid that uses glutamine as a nitrogen donor. alpha-KG is used as a carbon backbone for synthesis of glutamate, glutamine, arginine and proline. Proline can be synthesized from either ornithine by OAT or glutamate by the spontaneous cyclization of the intermediate glutamate γ-semialdehyde. Beside its synthesis by GDH, glutamate can also be generated from alpha-KG by action of BCAT1/2 using nitrogen from leucine, isoleucine and valine. Arginine is synthesized from glutamate via ornithine in the urea cycle. Arginine synthesis also requires aspartate nitrogen and the enzyme ASS1 and ASL. Two nitrogen groups of urea (for disposal) comes from the carbamoyl phosphate generated in the mitochondrial matrix from free ammonia via CPS I and aspartate which is also formed in the mitochondrial matrix from OAA. Reactions that are reversible are indicated by two-sided arrow heads. Free ammonium ions are indicated by NH4+ while the amino group donated from either glutamate or glutamine are colored in red. Abbreviations: Arg1, arginine 1; ASNS, asparagine synthetase; GLS, glutaminase; GLUD1, glutamate dehydrogenase 1; GS, glutamine synthetase; OTC, ornithine transcarbamylase; P5C, 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid; P5CS, pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase; PAH, phenylalanine hydroxylase; PHDGH, D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PRODH, proline dehydrogenase; PSAT1, phosphoserine aminotransferase 1; PSPH, phosphoserine phosphatase; PYCR, pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase.
