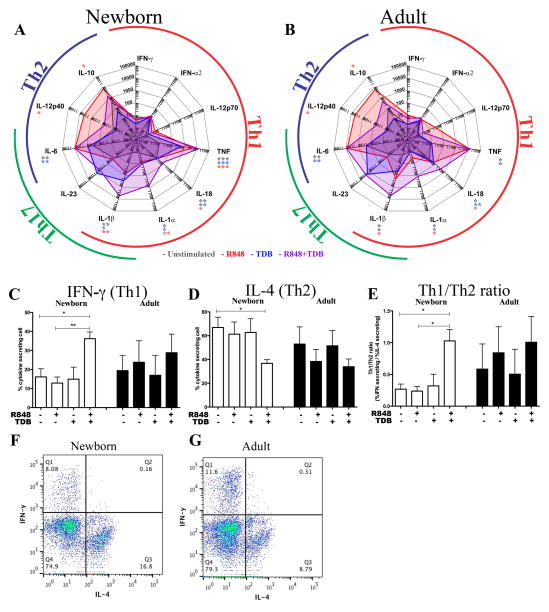
Figure 2. Dual stimulation using R848 and TDB shifts the pattern of cytokine production by human adult and newborn DCs and enables the polarization of newborn naïve CD4+ T cells to Th1 cells.
Adult and newborn DCs were stimulated with R848 (50 μM), TDB (100 μg/ml), or both (A+B). This restored TNF production to adult-like levels in newborn cells and enhanced production IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-18 (n=6, Paired Student’s t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). Naïve (CD4+CD45RA+CD45RO−) T cells were isolated, cultured in 10% (vol/vol) autologous plasma, and activated for 6 days with anti-CD3/CD28 beads, in the presence of culture supernatants of autologous MoDCs activated with agonists as indicated. After 6 days, IFN-γ- and IL-4-producing cells were quantified by flow cytometry following the addition of Brefeldin A. Mean relative percentage of IFN-γ producing cells (C), mean relative percentage of IL-4 producing cells (D), and ratio of IFN-γ producing cells over IL-4 producing cells (E) show an increase in Th1 polarization after treatment with culture supernatants from R848+TDB-activated MoDCs (n=4, Mean+SEM, paired Student’s t-test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). Representative images of flow cytometric quantification of IFN-γ and IL-4 producing cells are shown. Depicted are control samples of a representative newborn and adult whose T cells were activated with anti-CD3/28 in the presence of supernatant from unstimulated autologous MoDCs. (F–G).