Figure 6.
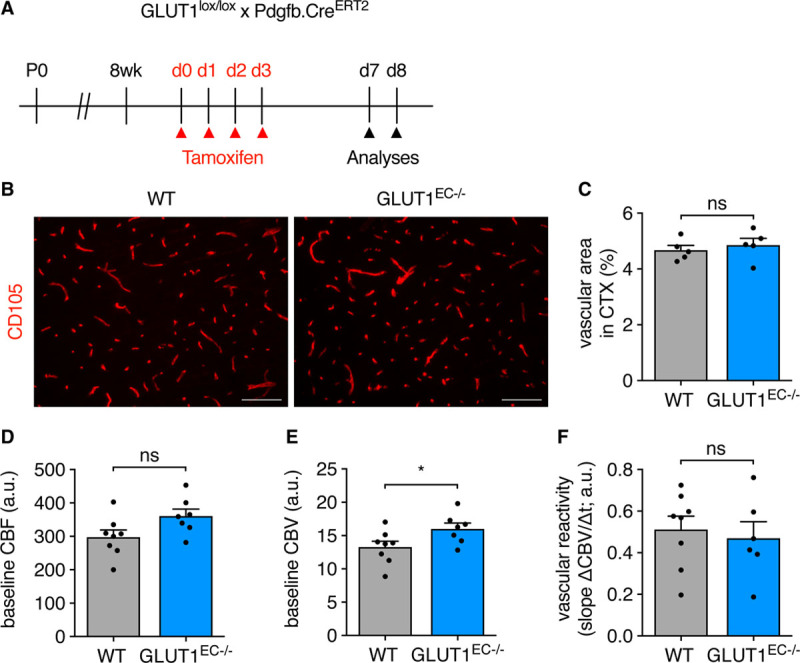
Loss of EC-GLUT1 (endothelial glucose transporter isoform 1) does not impair brain vascular function. A, Schematic representation of experimental timing for brain vascular analyses in adult GLUT1lox/lox×Pdgfb.CreERT2 mice. B and C, Representative pictures of the cluster of differentiation 105-stained cortical vasculature in adult GLUT1EC−/− mice vs wild-type (WT) littermates (B) and quantifications of vascular area (C; Student t test). D–F, Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) measurements in GLUT1EC−/− mice vs WT littermates for assessment of baseline cerebral blood flow (CBF; D), baseline cerebral blood volume (CBV; E), and for the determination of vascular reactivity, that is, dynamic CBV in response to the injection of the pharmacological vasodilator acetazolamide (F) (Student t test). Scale bar=100 µm (B). *P<0.05.
