Figure 4. Effects of ampicillin on colonic microbiota.
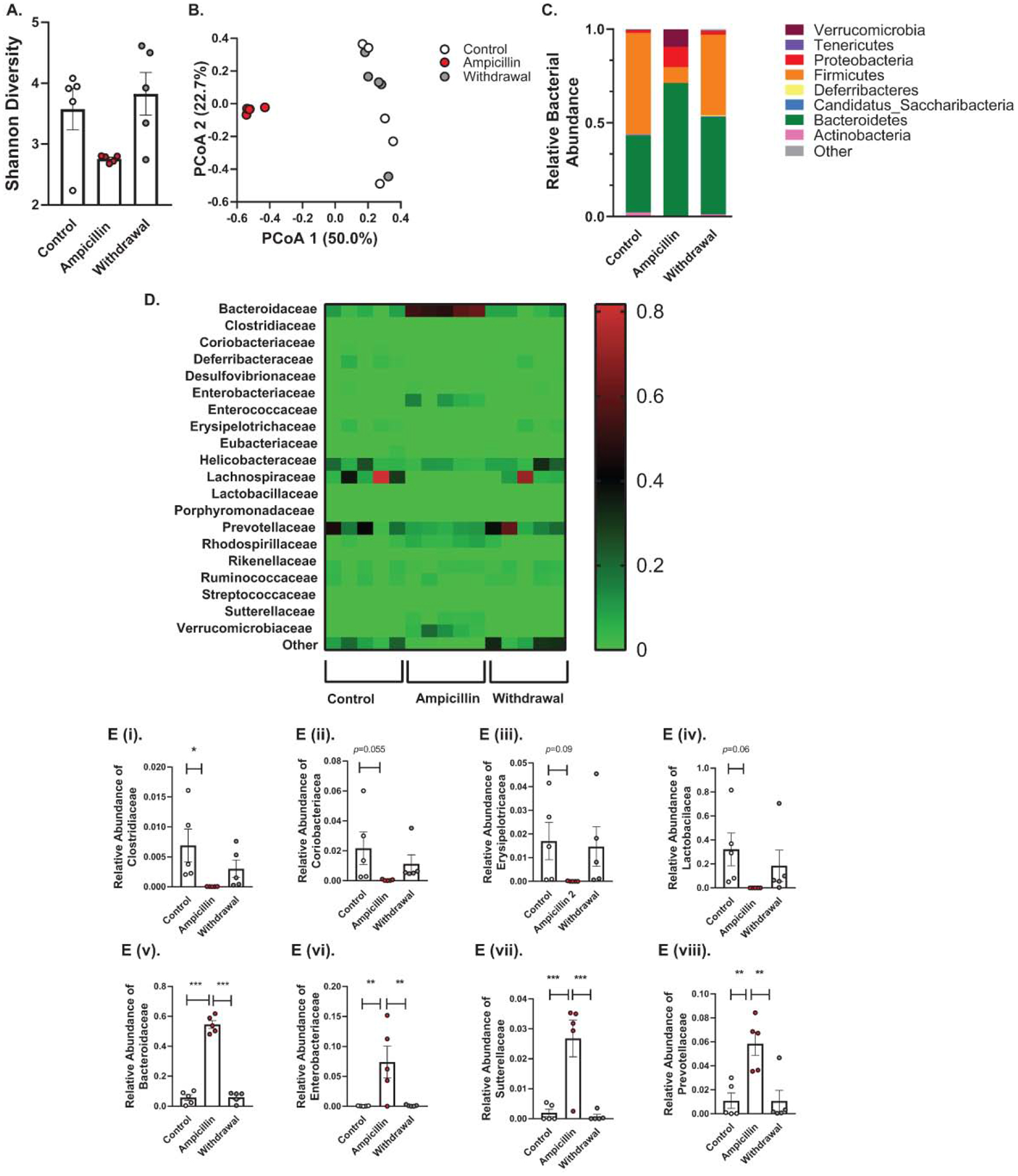
(A) Shannon diversity comparisons showed that alpha diversity decreased with ampicillin and increased 10 days after ampicillin discontinuation. (B) PCoA analysis using the weighted UniFrac suggested that the overall community composition from ampicillin group was different from control group or withdrawal group. (C) At the phylum level, treatment with ampicillin caused a significant increase in relative abundance of Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia and a significant decrease in Firmicutes and Actinobacteria, these changes were reversible after 10 days of ampicillin discontinuation. (D) Heatmap of differentially abundant OTUs in different groups at family level. E. Relative bacterial abundance at family level. The relative abundance of E (i) Clostridiaceae, E (ii) Coriobacteriacea, E (iii) Erysipelotricacea, and E (iv) Lactobacilacea and had a trend toward increase after ampicillin discontinution. E (v) Bacteroidaceae, E (vi) Enterobacteriaceae, E (vii) Suterellaceae, and E (viii) showed significant increase in relative abundance after ampicillin treatment, an effect which was reversed 10 days after stopping ampicillin.
