Figure 2. Deletion of Abl1 suppresses tumor development and prolongs survival in the MET/CAT-induced HCC mouse model.
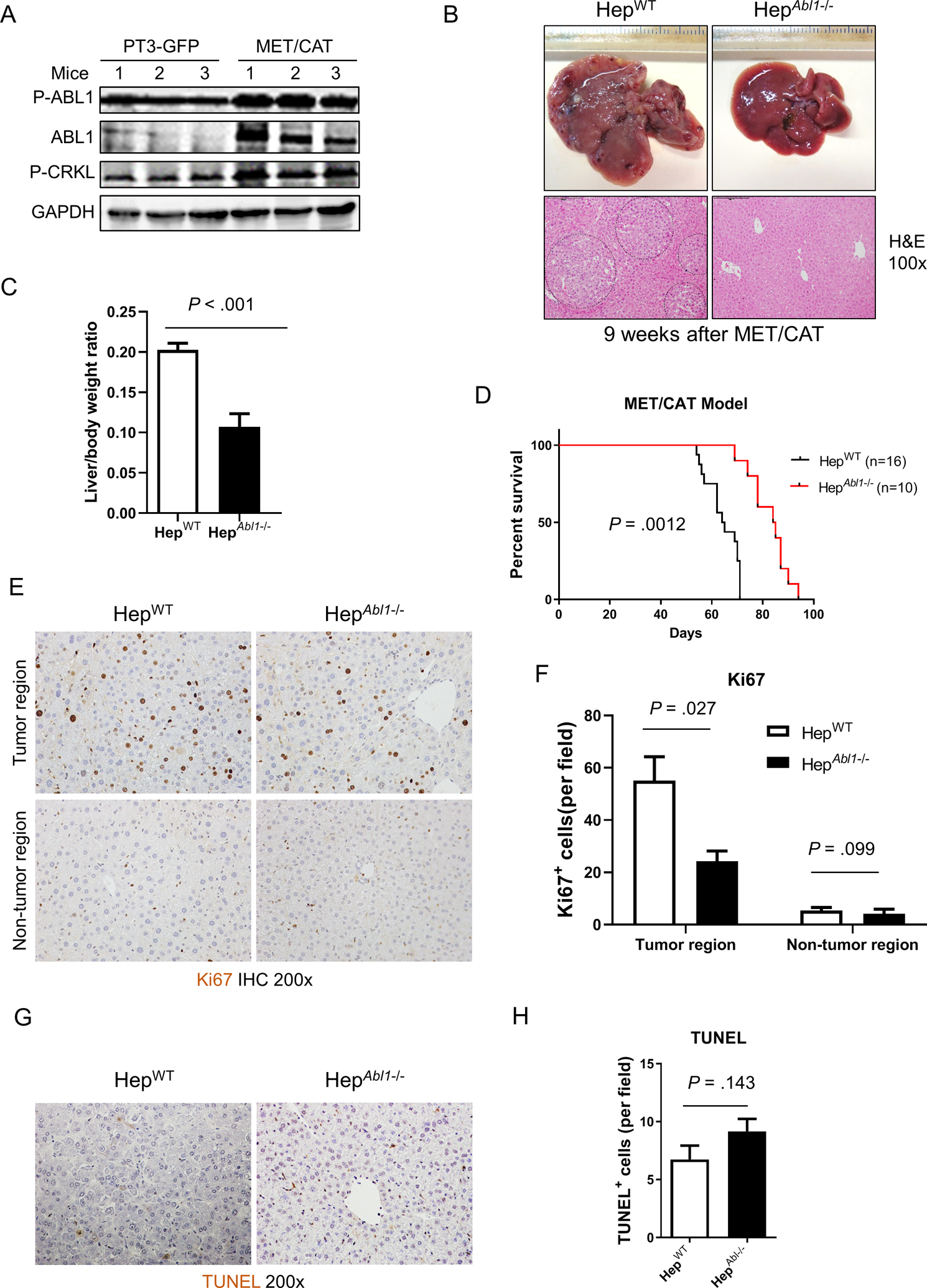
(A) Levels of p-ABL1 (p-Y412), ABL1, p-CRKL and GAPDH proteins in the livers of HepWT mice 9 weeks after hydrodynamic injection of MET/CAT or pT3-GFP. (B) Photographs and H&E staining of livers of HepWT and HepAbl1−/− mice 9 weeks after injection of MET/CAT. (C) Liver body/weight ratios were analyzed in the mice from (B) (n=6). (D) Survival curves of HepWT and HepAbl1−/− mice after injection of MET/CAT. (E) Hepatocyte proliferation of HepWT and HepAbl1−/− mice 9 weeks after injection of MET/CAT was examined by immunohistochemistry for Ki67. (F) Quantification of Ki67 staining for (E) (n=4). (G) Apoptosis in the livers of HepWT and HepAbl1−/− mice 9 weeks after injection of MET/CAT was examined by TUNEL staining. (H) Quantification of TUNEL staining for (G) (n=4).
