Figure 4. ABL1 Knockdown inhibits HCC cell proliferation by decreasing NOTCH1 expression.
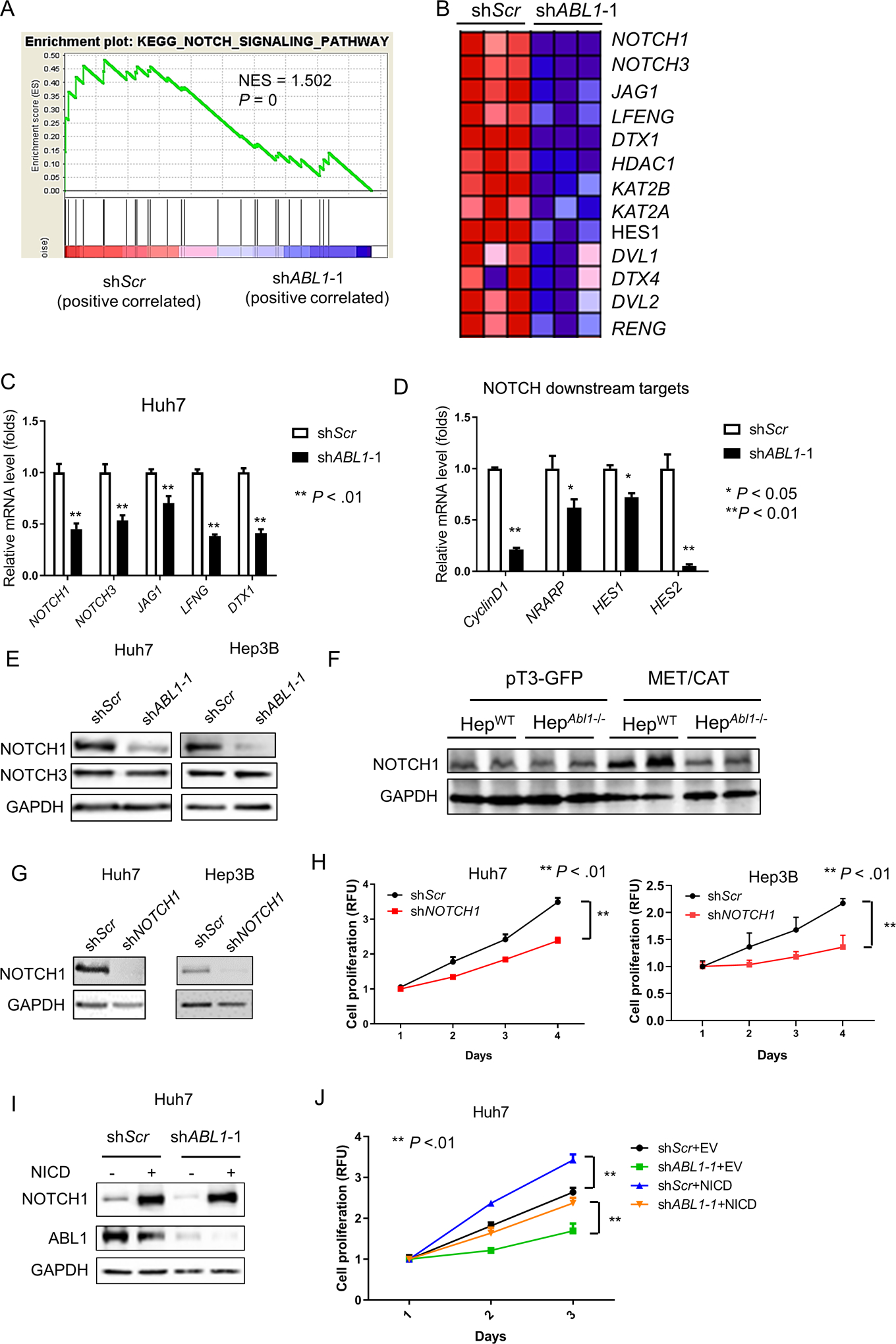
(A) GSEA shows that the NOTCH signaling pathway is enriched in ABL1-KD Huh7 cells. (B) A heat-map indicates the expression of genes in the NOTCH signaling pathway is decreased by ABL1 knockdown in Huh7 cells. (C) Relative mRNA levels of genes in the NOTCH signaling pathway in scrambled-RNA and ABL1-KD Huh7 cells. (D) Relative mRNA levels of NOTCH downstream targets in the scrambled-RNA and ABL1-KD Huh7 cells. (E) NOTCH1, NOTCH3 and GAPDH protein expression in scrambled-RNA and ABL1-KD HCC cells was determined by Western blotting. (F) Expression of NOTCH1 and GAPDH proteins in whole livers of HepWT and HepAbl1−/− mice injected with pT3-GFP or MET/CAT for 9 weeks was determined by Western blotting. (G) NOTCH1 and GAPDH protein expression in scrambled-RNA and NOTCH1-KD Hep3B and Huh7 cells was determined by Western blotting. (H) Quantification of cell proliferation from scrambled-RNA and NOTCH1-KD HCC cells at different time points after seeding. (I) Expression of NOTCH1, ABL1 and GAPDH proteins in control (infected with EF.CMV.GFP) and NOTCH1-overexpressed (infected with EF.hICN1.CMV.GFP) Huh7 scrambled and ABL1-KD cells was determined by Western blotting. (J) Quantification of cell proliferation from control and NOTCH1-overexpressed Huh7 scrambled and ABL1-KD cells at different time points after seeding.
