Figure 7. ABL1 inhibitors suppress human HCC growth in vitro and in vivo.
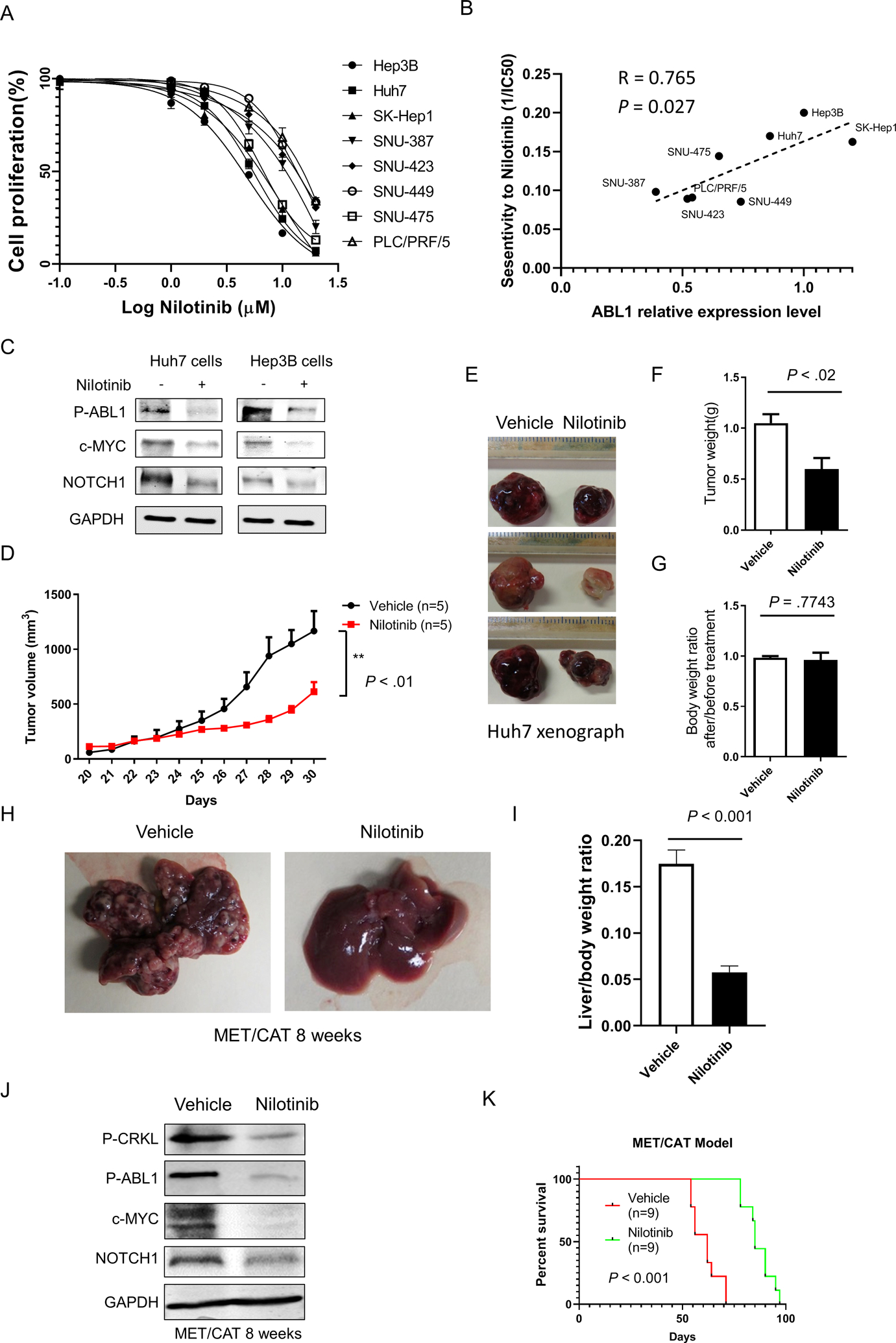
(A) Quantification of cell proliferation of HCC cells treated with vehicle or nilotinib at different dose after 48 hours treatment. (B) Correlation between ABL1 expression and sensitivity to nilotinib in HCC cells described in A. (C) Levels of p-ABL, c-MYC, NOTCH1, and GAPDH proteins in HCC cells treated with vehicle or 5μM Nilotinib for 24h. (D) SCID-bg mice injected with Huh7 cells were gavaged with vehicle or nilotinib for 10 days and Tumor volumes from mice (n=5/group) were measured. (E) Gross images of tumors from vehicle- or nilotinib-gavaged animals are shown. (F) Tumor weights from mice from D. (G) Body weight ratios from mice after/before nilotinib treatment. (H) C57BL/6 mice were injected with MET/CAT to induce HCC. Four weeks after such injection, the mice were gavaged with vehicle or nilotinib for 4 weeks (some mice treated with vehicle had to be euthanized earlier due to tumor burdens), and gross images of livers from vehicle- and nilotinib-gavaged animals at 8 weeks after MET/CAT injection are shown. (I) Liver/body weight ratios from the mice as (I) (n=6/group). (J) Levels of p-CRKL, p-ABL, c-MYC, NOTCH1, and GAPDH proteins in the mouse livers from H. (K) Survival graphs for mice gavaged with vehicle or nilotinib (n=9/group).
