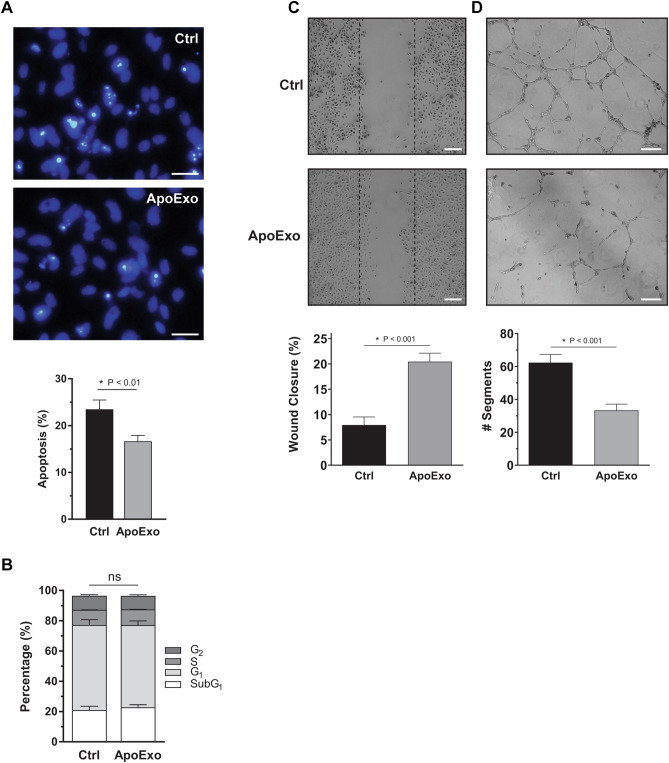
Figure 2.
Apoptotic exosome-like vesicles inhibit apoptosis, improve wound closure, and decrease angiogenic activity in endothelial cells. (A) Apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) increased cell survival under serum starvation. Evaluation by Hoescht and Propidium iodide (HO/PI) staining of apoptotic or necrotic cells in serum-starved endothelial cells exposed for 4 h to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) (Scale bar: 25 µm). HO/PI experiments expressed as the percentage of apoptosis ± SEM. n = 11 for each condition. (B) ApoExo did not affect the cell cycle. Cell cycle analysis by PI staining of endothelial cells under serum starvation exposed for 12 h to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo). Cell cycle experiments expressed as the percentage of cells under each cycle stage ± SEM. n = 3 for each condition. (C) ApoExo increased wound closure. Serum-starved endothelial cells were mechanically injured and exposed to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo). Wound closure was followed over a 12 h period (Scale bar: 200 µm). Wound healing assay expressed as the percentage of wound closure ± SEM. n ≥ 6 for each condition. Representative pictures at 12 h post-injury are presented. (D) ApoExo decreased tubules formation of endothelial cells. Serum-starved endothelial cells were exposed to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) and capillary-like structures were quantified following a 7 h treatment on extracellular matrix (Scale bar: 200 µm). Capillaries density is depicted as the number of segments per field ± SEM and representative pictures of tubule formations are presented. n ≥ 3 for each condition. P values obtained by unpaired t-test.