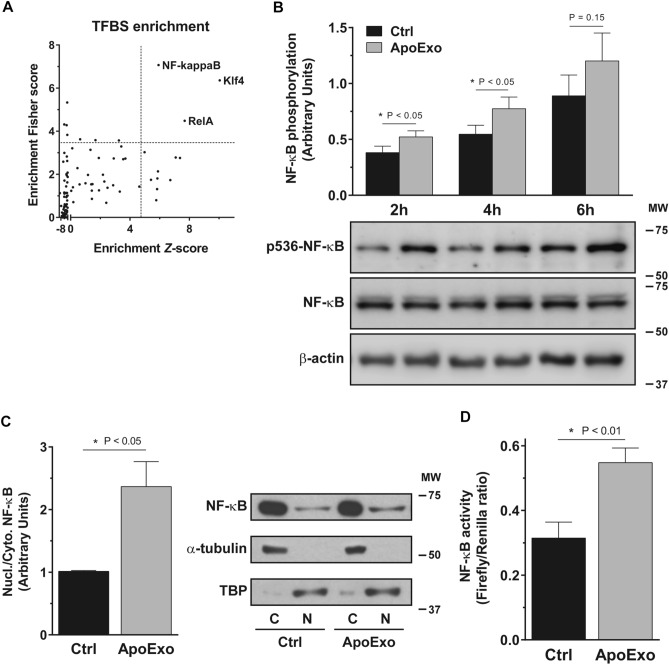
Figure 4.
Apoptotic exosome-like vesicles trigger the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) NF-κB transcription factors family binding sites are enriched on the promoter of differentially expressed genes. Differentially expressed protein-coding genes from RNA-sequencing analysis were processed through oPOSSUM 3.0 using single-site analysis. The transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) were then classified according to their Fisher score and Z-score. TFBS were considered overrepresented when both scores > mean score + 1.5 fold standard deviation (dot lines). (B) Apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) increase NF-κB phosphorylation in endothelial cells. Serum-starved endothelial cells were exposed to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) and phosphorylation of NF-κB at Ser536 (p536-NF-κB) was followed from 2 to 6 h. NF-κB phosphorylation was quantified by the phospho-to-total ratio for each time point and expressed as arbitrary units ± SEM. n ≥ 11 for each condition. Representative immunoblots cropped from the same gel are presented. (C) ApoExo trigger NF-κB translocation in endothelial cells. Serum-starved endothelial cells were exposed to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) for 4 h and NF-κB (RelA) expression was assessed. NF-κB translocation was quantified by the nuclear (N) to cytoplasmic (C) ratio and expressed as arbitrary units ± SEM. n = 6 for each condition. Representative immunoblots cropped from the same gel are presented. (D) ApoExo increase NF-κB activity in endothelial cells. Serum-starved endothelial cells were exposed to the vehicle (Ctrl) or apoptotic exosome-like vesicles (ApoExo) for 4 h and NF-κB activity was expressed as Firefly/Renilla luciferases ratio ± SEM. n = 6 for each condition. P values obtained by a one-tailed unpaired t-test. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 12.