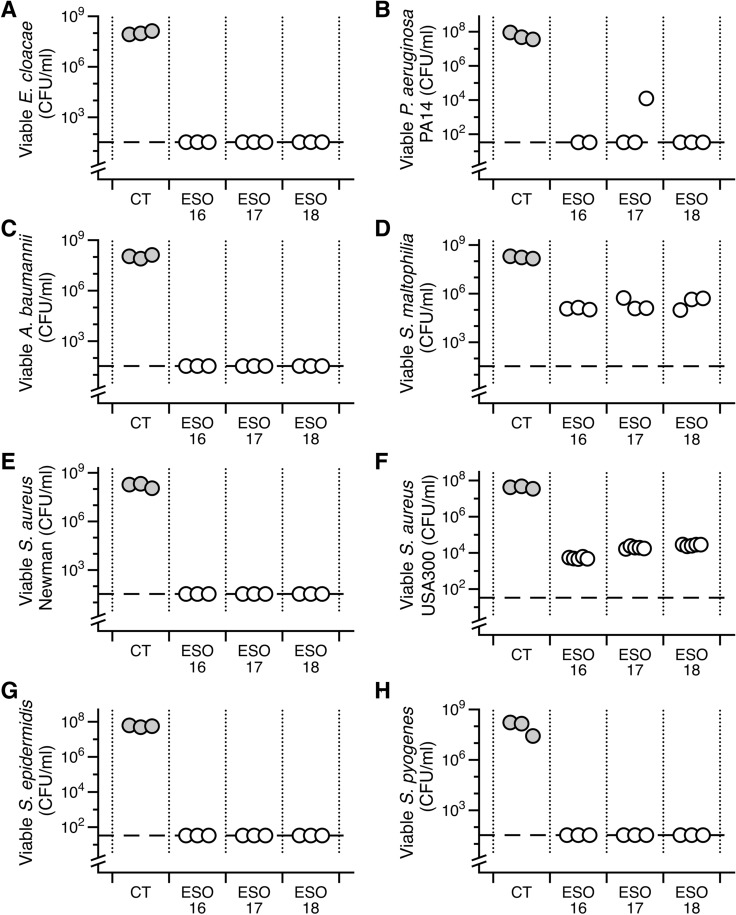
Figure 3.
Bald’s eyesalve (ESO) activity against eight example strains of bacteria that commonly cause chronic wound infections. Planktonic cultures were grown for 6 h in synthetic wound fluid. Cultures were treated with ESO (batches 16–18) or sterile water (CT) to a final concentration of 33% v/v (n = 3–5 replicates per treatment). After 18 h bacteria were recovered for CFU counts. The dashed line represents the limit of detection by plating. For S. maltophila and S. aureus USA300, where we did not observe complete killing, we used ANOVA to determine that the CFU recovered from ESO-treated wounds was significantly different from control wounds (S. aureus USA300: F2,14 = 3,458, p < 0.001; S. maltophilia: F3,8 = 87.41, p < 0.001). Data were log transformed to meet the assumptions of linear modelling. A Dunnett’s test was conducted to compare the CFU of the three batches with the CFU of the controls. All 3 batches of ESO were significantly different from their respective controls for both isolates (all p < 0.001). Raw data and R scripts are supplied in the Data Supplement.