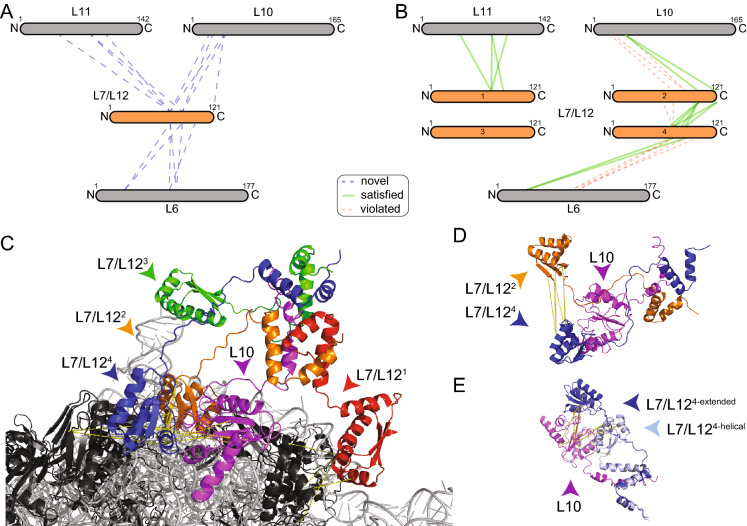
Figure 3.
The dense interaction network of L7/L12 captured by XL-MS. Ribosomal proteins (black) and rRNA (grey) are shown in cartoon. Cross-linked proteins are color highlighted. Cross-links are shown as dotted lines, satisfaction (yellow) or minor violation (orange) are indicated. (A) Interaction network of L7/L12. Sizes of the boxes are scaled to the length of the protein sequences; each dotted line represents one identified novel cross-link pair. (B) Satisfied cross-links after remodeling; Only 4 cross-links of L6 to L7/L12 could not be unambiguously mapped (not shown); In addition, 5 intra-links show violation in the monomer, but satisfaction in the L7/L12 multimer. (C) Model of the interaction of an L7/L12 tetramer (blue, green, red, orange) bound to the helix 8 of L10 (magenta) based on the cross-linking information (see text). (D) Satisfaction of intra-molecular cross-links between CTD domains of L7/L12. (E) Inter-molecular cross-links satisfying both extended and helical conformation of the linker region of L7/L12; Note that all cross-links are satisfied in the helical linker conformation, and all but one cross-link are satisfied in the extended conformation. The images of protein structures were generated with PyMOL (Version 2.3.2), Schrödinger, LCC. https://pymol.org.