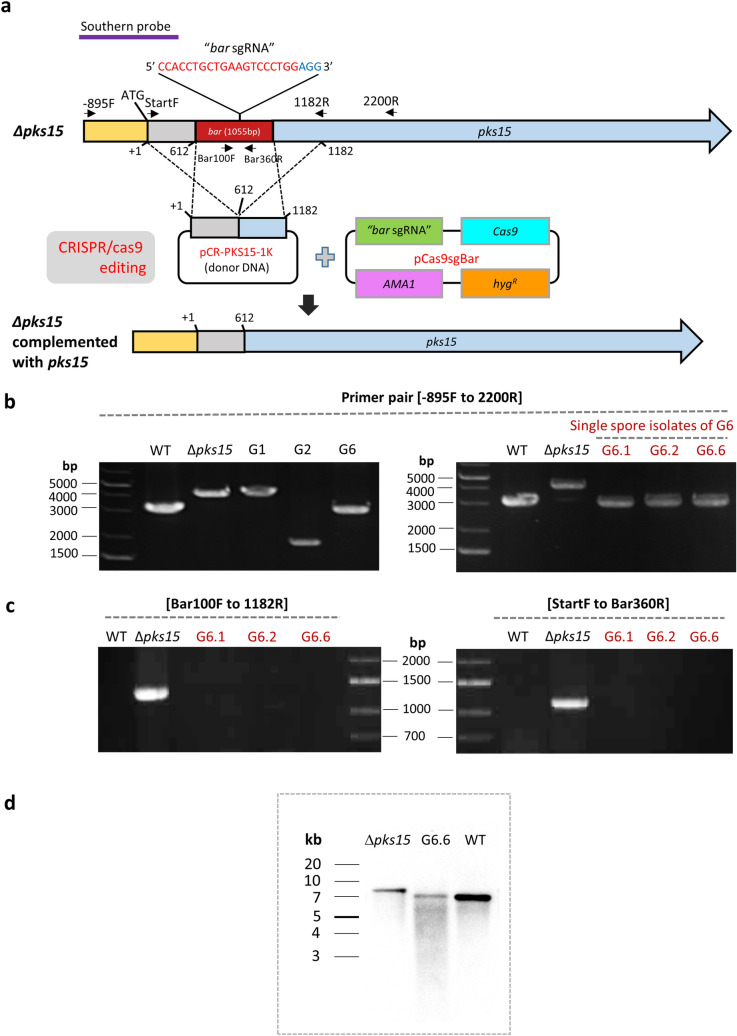
Figure 1.
(a) A schematic diagram of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in the ∆pks15 mutant by targeting the selection marker gene bar that was used to disrupt pks15. An in-cis complementation of the ∆pks15 mutant was performed by homologous recombination with a wild-type copy of pks15 using the donor DNA pCR-PKS15-1K. Molecular analysis of the pks15 locus of transformants G1, G2 and G6 (from genetic complementation of ∆pks15) was compared to those for the wild type (WT) and Δpks15 using PCR (b, c) and Southern (d) analyses. Primers used for PCR and their locations are shown in (a). (b) PCR amplification with primers PKS15-minus-895F and PKS15-2200R primer. (c) PCR amplifications with primers Bar100F and PKS15-1182R, and PKS15-StartF and Bar360R. (d) Southern blotting results for Δpks15, the complemented isolate G6.6 and the wild type. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with a pks15-specific probe, shown in (a).