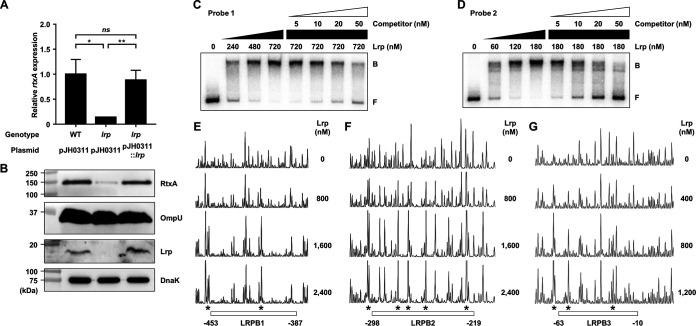
FIG 2.
Effects of the lrp mutation on the rtxA expression and specific binding of Lrp to the PrtxA regulatory region. (A and B) Total RNAs and proteins were isolated from the V. vulnificus strains grown to an A600 of 0.5 and used to determine the rtxA transcript and RtxA, OmpU, Lrp, and DnaK protein levels. (A) The rtxA transcript levels were determined by qRT-PCR analyses, and the rtxA transcript level in the wild type was set at 1. Error bars represent the SD. Statistical significance was determined by the Student’s t test (**, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant). (B) The secreted levels of RtxA and OmpU (as an internal control) and cellular levels of Lrp and DnaK (as an internal control) were determined by Western blot analysis. Molecular size markers (Bio-Rad) are shown in kilodaltons. WT (pJH0311), wild type; lrp (pJH0311), lrp mutant; lrp (pJH0311::lrp), lrp complemented strain with pZW1818. (C and D) Each 452-bp DNA probe of the PrtxA regulatory region (probe 1 for panel C and probe 2 for panel D; 5 nM) was radioactively labeled and then incubated with increasing amounts of Lrp as indicated. For competition analysis, various amounts of the same but unlabeled DNA fragment were used as a self-competitor and added to the reaction mixture containing the 5 nM labeled DNA before the addition of 720 nM (C) or 180 nM (D) Lrp. The DNA-protein complexes were separated by electrophoresis. B, bound DNA; F, free DNA. (E to G) The same DNA probes of each PrtxA regulatory region (40 nM) were labeled with 6-FAM, incubated with increasing amounts of Lrp as indicated, and then digested with DNase I. The regions protected by Lrp are indicated by white boxes (LRPB1, LRPB2, and LRPB3), respectively. The nucleotides showing enhanced cleavage are indicated by asterisks. Nucleotide numbers shown are relative to the transcription start site of rtxA.