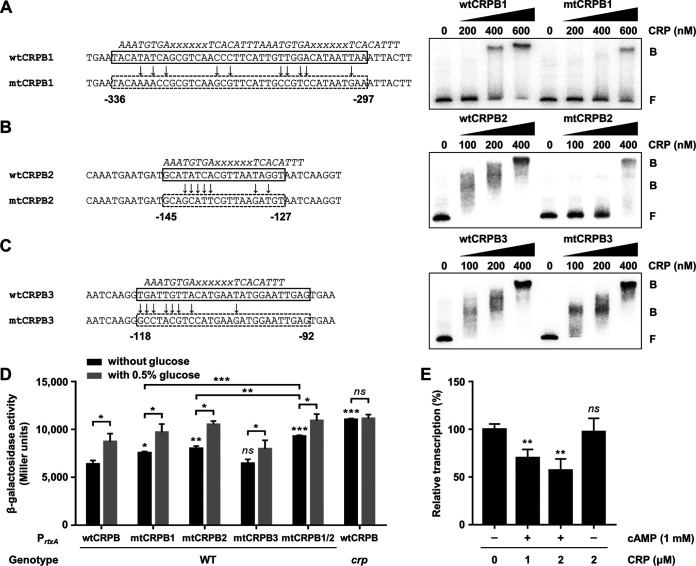
FIG 7.
Effect of CRP binding on the PrtxA activity. (A to C) The CRP-binding sequences wild-type CRPB1 (wtCRPB1) (A), wtCRPB2 (B), and wtCRPB3 (C) in the PrtxA regulatory region are indicated by solid boxes. The mutated CRPBs (mtCRPBs) are indicated by dashed boxes, respectively, with the site-directed mutagenized nucleotides marked by arrows. The consensus sequences for CRP binding are indicated by italicized letters above the wtCRPBs. x, any nucleotide. Nucleotide numbers shown are relative to the transcription start site of rtxA. For EMSAs, each radiolabeled DNA probe of wtCRPB or mtCRPB (5 nM) was incubated with increasing amounts of CRP as indicated. The DNA-protein complexes were separated by electrophoresis. B, bound DNA; F, free DNA. (D) The V. vulnificus strains harboring reporter plasmids with promoterless lacZ fused to PrtxA carrying either wild-type or mutated CRPB as described in panels A to C were grown to an A600 of 0.5 with or without 0.5% glucose. The β-galactosidase activities of the V. vulnificus cells were measured and expressed in Miller units. Error bars represent the SD. Statistical significance was determined by the Student’s t test (***, P < 0.0005; **, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant relative to the wild-type strain with PrtxA carrying wtCRPB). WT, lacZ mutant harboring the reporter plasmid with promoterless lacZ fused to PrtxA carrying wtCRPB or mtCRPB; crp, crp lacZ double mutant harboring the reporter plasmid with promoterless lacZ fused to PrtxA carrying wtCRPB. (E) In vitro transcription of rtxA. An 881-bp rtxBDE-rtxHCA intergenic region spanning from positions −629 to +252 relative to the transcription start site of rtxA was used as a template DNA and transcribed in vitro with CRP in the presence or absence of cAMP as indicated. Relative transcription levels were determined using the heights of rtxA transcript peaks measured in arbitrary fluorescent units and expressed using the transcription level from the reaction without CRP as 100%. Error bars represent the SD from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (**, P < 0.005; ns, not significant relative to the transcription level from the reaction without CRP).