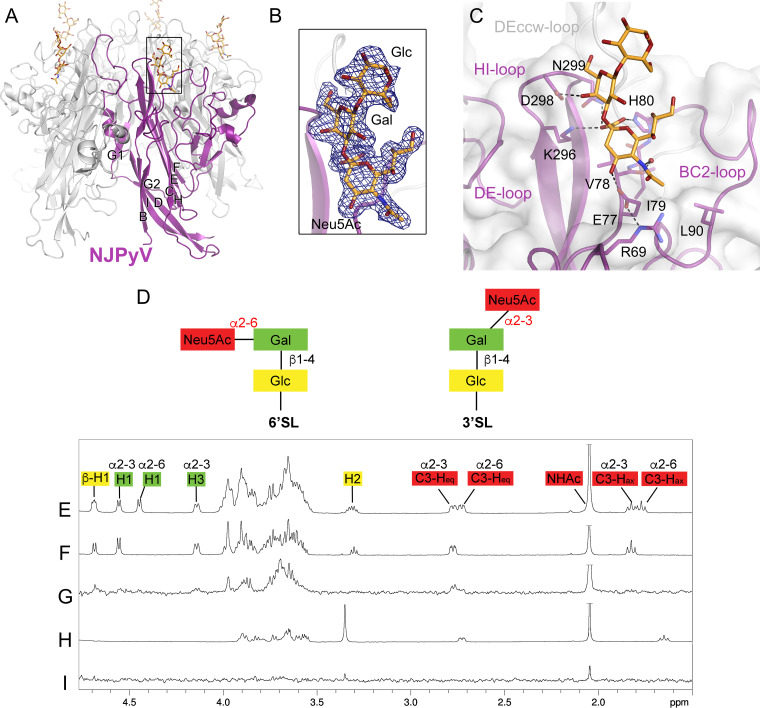
FIG 1.
NJPyV VP1 engages the Neu5Ac-α2,3-Gal motif of 3′SL. (A) Structure of the NJPyV VP1 pentamer structure in complex with the 3′SL glycan. One VP1 monomer is highlighted in purple, the others are colored in gray. Glycans are shown in stick representation with carbons in orange, oxygens in red, and nitrogens in blue. (B) The simulated annealing difference electron density map for the 3′SL is contoured at a σ level of 2.5 and is shown with a radius of 2 Å around the ligand. (C) Interactions of NJPyV with 3′SL. Side chains of VP1 in the binding site are shown as sticks, and water molecules are shown as a red sphere. Direct and water-mediated interactions are indicated with dashed lines. (D) Schematic representation of the glycans, 3′SL and 6′SL, used for NMR experiments. Glc, glucose; Gal, galactose; Neu5Ac, N-5-acetyl neuraminic acid. (E) 1H NMR reference spectrum of 27 μM NJPyV VP1 with 1 mM 6′SL and 1 mM 3′SL. The equatorial H3 resonance of α2,3-linked-Neu5Ac is slightly shifted with respect to the same resonance of α2,6-Neu5Ac. (F) 1H NMR reference spectrum of 1 mM 3′SL. (G) STD NMR difference spectrum of the same sample as shown in panel D. (H) 1H NMR reference spectrum of 2 mM 2-O-methyl sialic acid and 27 μM NJPyV VP1. (I) STD NMR difference spectrum of the same sample as shown in panel G. Neu5Ac amide methyl group resonances are truncated.