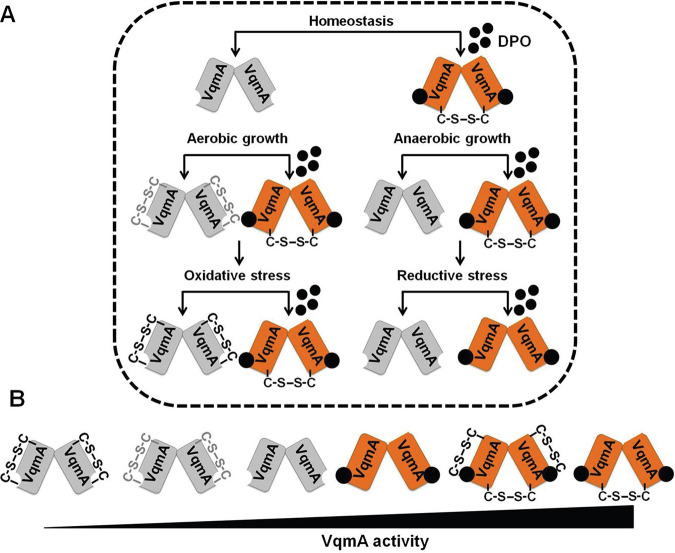
FIG 7.
Model depicting VqmA as a hub protein that compiles quorum sensing, environmental, and host information. (A) VqmA can exist in different states in vivo depending upon the availability of the DPO ligand and the cellular redox state. Thus, Apo-VqmA forms the C48-C63 intramolecular disulfide bond that suppresses its ability to bind DNA. Apo-VqmA activity is high under reducing growth conditions in which formation of the intramolecular C48-C63 bond is inhibited. Holo-VqmA forms the C134-C134 intermolecular disulfide bond that promotes DNA binding. Reductive stress disrupts the formation of the intermolecular disulfide bond. We propose that growth in the presence of bile salts imposes reductive stress, disrupts the formation of the C134-C134 intermolecular disulfide bond, and restricts VqmA DNA binding, thereby promoting virulence and biofilm formation. The gray and black intramolecular disulfide bonds denote partially oxidized and fully oxidized VqmA, respectively. (B) Relative VqmA activity levels as a consequence of disulfide bond formation. For simplicity, the fourth and fifth species in panel B are not displayed in panel A.