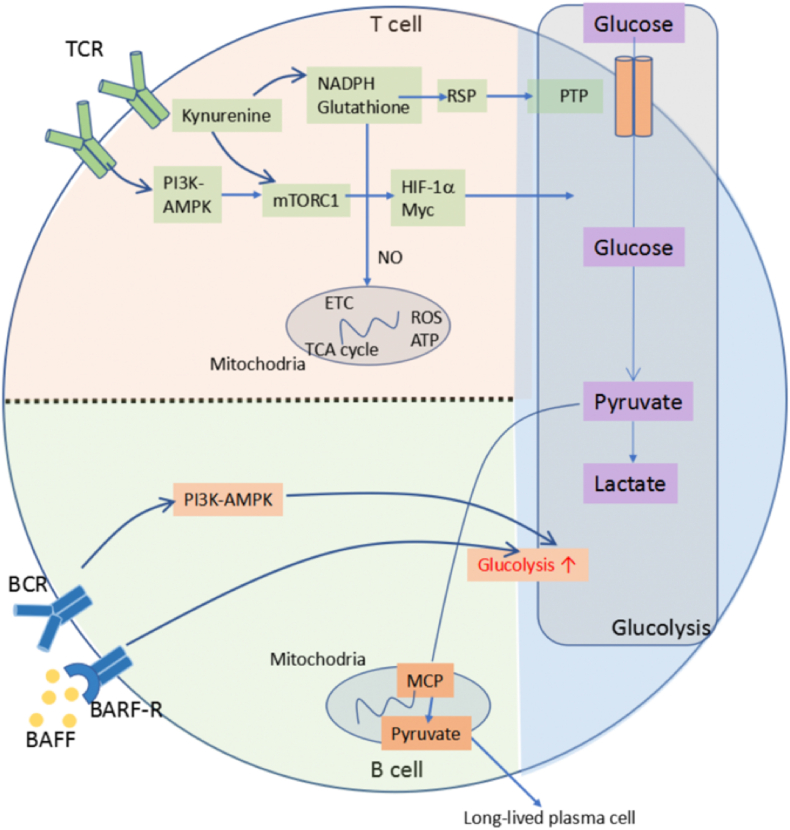
Fig. 2.
Glucose metabolic pathways in immune cells. The glucose metabolic pathway includes both glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation activates mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) through PI3K-AMPK pathway. Low levels of NADPH and glutathione leads to increased levels of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreased levels of ATP. It also contributes to mTORC1 activation, directly or through elevated levels of kynurenine. mTORC1 activation facilitates glucose metabolism through hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and Myc. In B cells, B cell activating factor (BAFF) and B cell receptor (BCR) signals increase glucose metabolism and glycolysis. This promotes pyruvate influx into the mitochondria, which is essential for the survival of long-lived plasma cells.