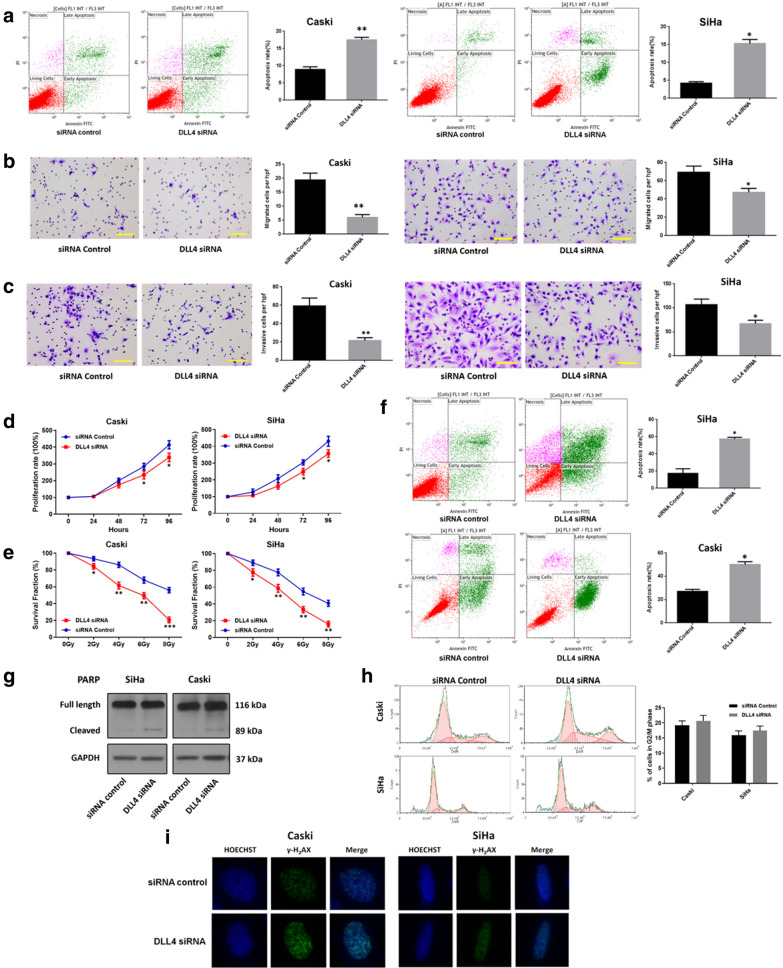
Fig. 2.
DLL4 downregulation induces cell apoptosis, inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion, increased the radiosensitivity in the cervical cancer cells. a, f Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) double-staining apoptosis assay showed that DLL4 downregulation induced cell apoptosis and stimulated radiation-induced apoptosis significantly compared with the control group in Caski and SiHa cells. b Migration ability and c invasion ability of Caski and SiHa cells were detected using the Transwell assay. The migrated and invaded cells of the DLL4 siRNA groups were significantly less compared with those of the control group. d, e The CCK8 assay was performed to detect the proliferation ability of CC cells. DLL4 downregulation inhibited cell proliferation and induced radiation-induced cell death compared with the control group in Caski and SiHa cells. g Western blot was used to assess the effect of DLL4 downregulation on the expression level of full-length and cleaved PARPs in the irradiated Caski and SiHa cells. GAPDH was used as a loading control. h The Cell cycle analysis showed that DLL4 downregulation did not significantly stimulate radiation-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest compared with the vector controls in the irradiated Caski and SiHa cells. i γH2AX foci analysis by immunofluorescence was conducted to detect the function of DLL4 on the regulation of DNA damage repair. DLL4 downregulation increased the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) caused by irradiation, suggesting that the repair of DNA DSBs was delayed by DLL4-siRNA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001