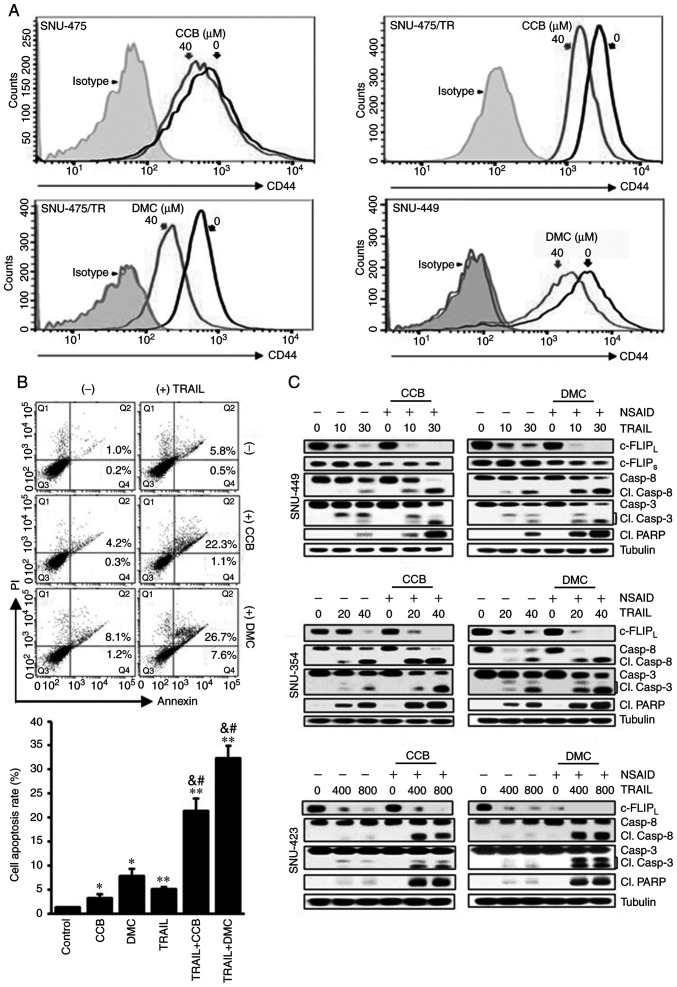
Figure 5.
Acceleration of TRAIL-mediated caspase and PARP activities by CCB in HCC cells through inhibition of CD44 surface expression and downregulation of c-FLIP. (A) SNU-475, SNU-475/TR and SNU-449 cells treated with 40 µM CCB or DMC for 24 h were stained with anti-CD44 antibody to determine the surface expression of CD44 by a flow cytometer. (B) Apoptosis assay. SNU-449 cells treated with TRAIL (30 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of NSAID (20 µM CCB or DMC). Annexin V/PI double staining by flow cytometry (upper image). Statistical analysis of the cell apoptosis assay (lower histogram). The number of apoptotic cells is the sum of Q2 and Q4. Data are mean ± SD, n=3. *P<0.01, **P<0.001 vs. the control; &P<0.001 vs. TRAIL alone; #P<0.001 vs. CCB or DMC alone, respectively. (C) SNU-449, SNU-354 and SNU-423 cells treated with the indicated doses of TRAIL (ng/ml) in the presence or absence of NSAID (20 µM CCB or DMC) for 24 h. The levels of c-FLIP and activity of caspase and PARP in these cells were determined by western blot analysis. Cl., cleaved; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; CCB, celecoxib; DMC, 2,5-dimethyl celecoxib; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; NSAID, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; c-FLIP, cellular-FLICE inhibitory protein.