Fig. 1 |. Fundamental mechanisms underlying representative photonic healthcare applications.
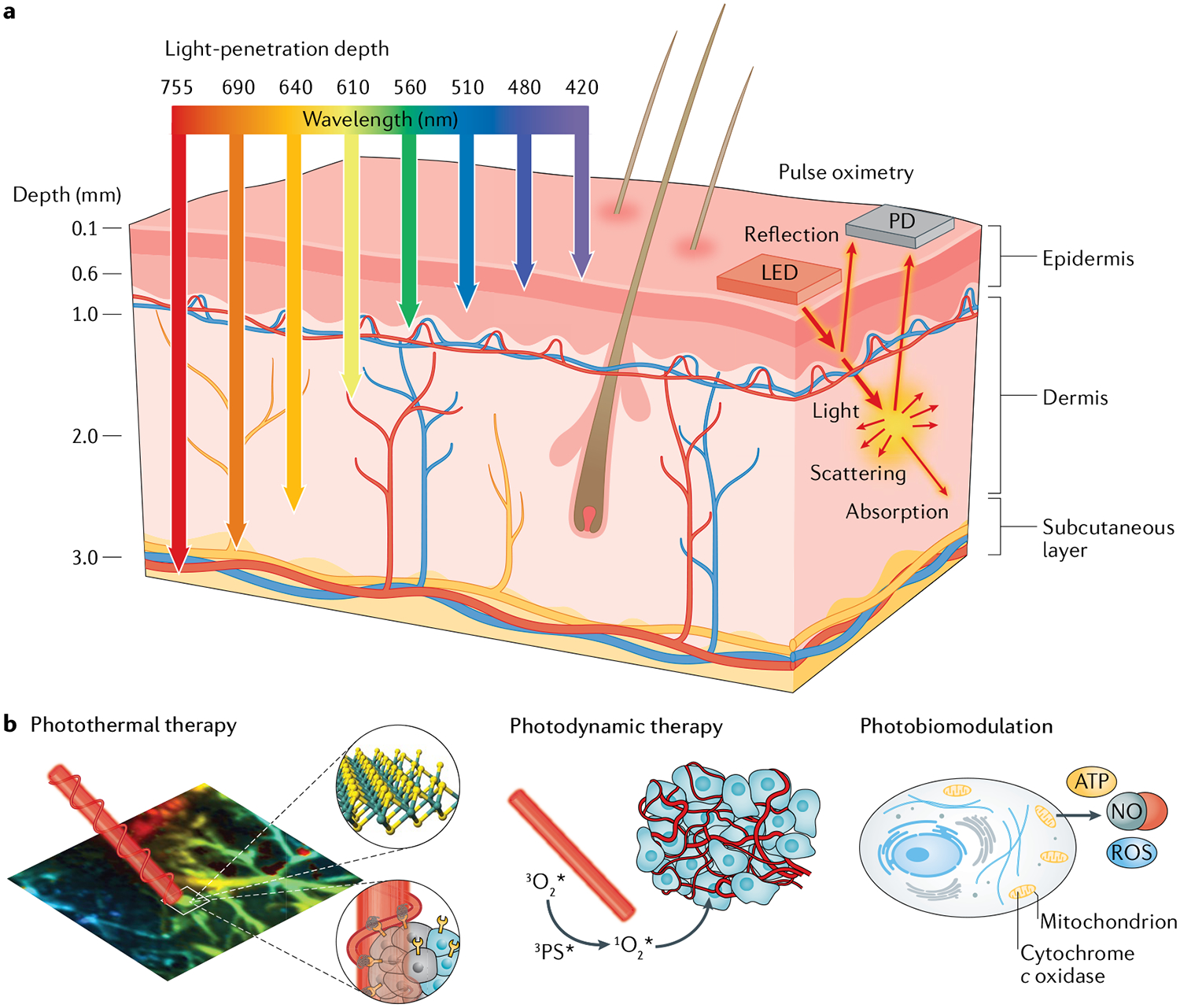
a | Schematic illustration of wavelength-dependent light-penetration depth and of photonic diagnosis via pulse oximetry, in which light absorption is detected in peripheral blood using a light-emitting diode (LED) and a photodetector (PD). b | Schematic illustrations of: photothermal therapy, in which light-triggered thermal ablation is used on diseased tissues; photodynamic therapy, which uses reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by a photosensitizer; and photobiomodulation, which uses photonic stimulation of mitochondrial chromophores to produce nitric oxide (NO) and ROS. ATP, adenosine triphosphate.
