Figure 4: Stem cell-based therapy, gene transfer and epigenetic therapy as promising innovative strategies for treating pulmonary hypertension.
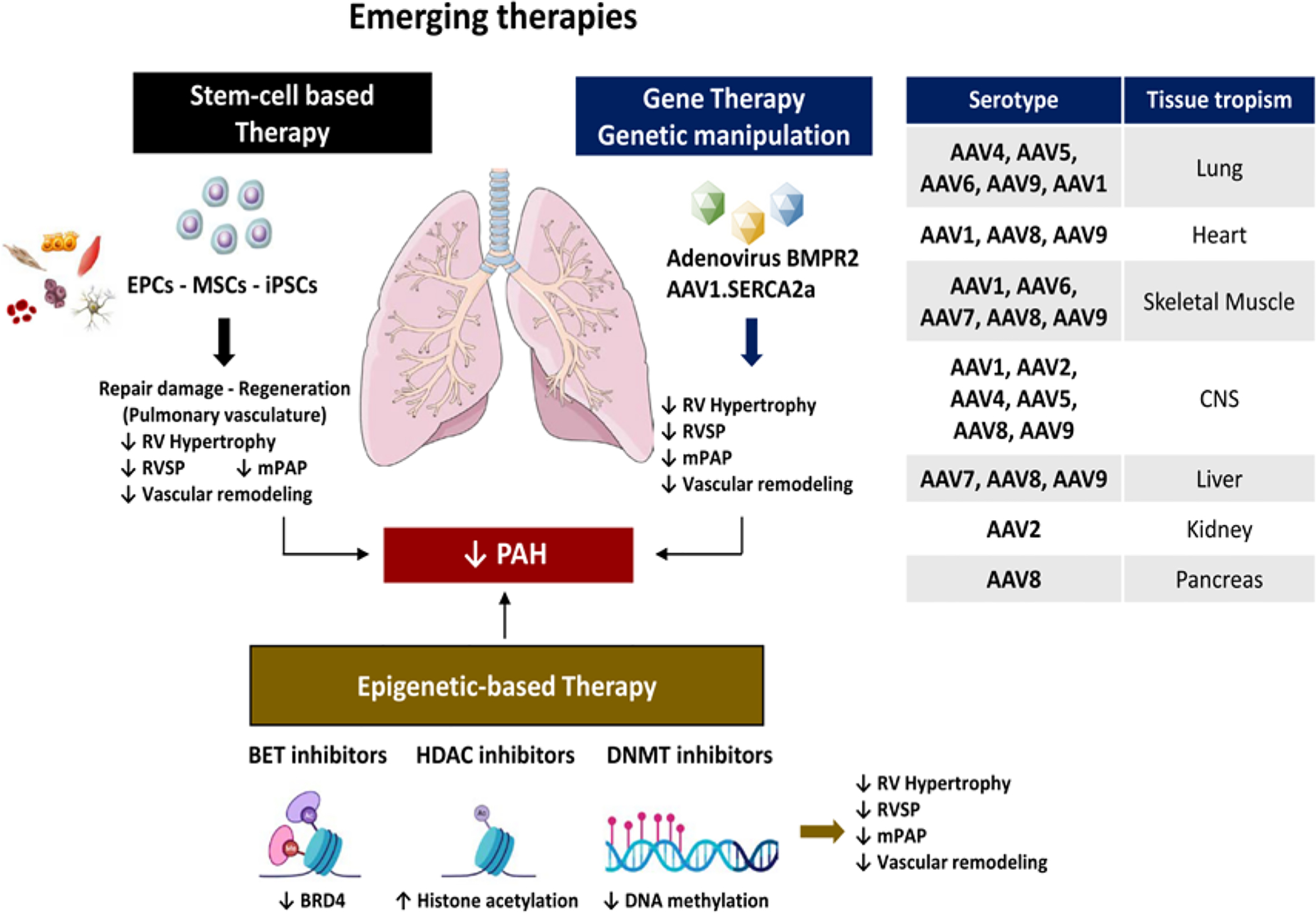
Recent preclinical studies suggested that stem cell-based therapies, gene transfer and epigenetic-based therapies may offer a new perspective in the treatment of PAH. Administration of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), intratracheal administration of inhaled-adenovirus encoding for BMPR2 or gene delivery of adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 1 encoding for human SERCA2a prevented and reversed the development of PH in preclinical animal models of PAH by blocking cardiac/arterial remodeling and improving hemodynamic abnormalities (RVSP, mPAP). Increasing evidence suggests that epigenetic-based therapies, such as DNMT, HDAC and BET inhibitors, may be of great therapeutic potential for treating PAH.
