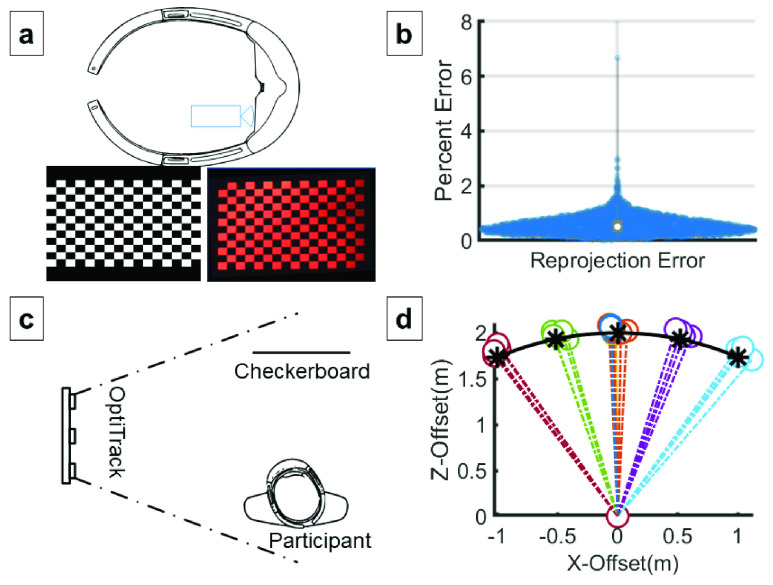
FIGURE 2.
Image Quality (a) Head mounted display (HMD) geometric distortion error was measured by displaying a  checkerboard image (red channel only) of known dimensions and capturing its resulting display with a calibrated camera placed at user’s eye position. Twelve different checkerboard poses were captured. The captured images were processed by a corner detection algorithm to generate detected positions for comparison against the known corner positions in the reference images. The corner positions were least-square fit by a geometric transform for all patterns compensate for camera misalignment to produce the error distribution shown, normalized to the checkerboard size (b). Mean, SD of reprojection error was 0.52%±0.31%. An erroneous corner detection result in one of the images caused a single false 6.64% distortion outlier. (c) During human in the loop accuracy testing, a user aligned virtual checkerboard images placed at various orientations with a physical checkerboard poster affixed to a wall at eye level. An optical tracker with clear line of sight to user and target, recorded the position of the user as they moved to align the image. (d) The summary plot shows the results for seven different image poses of the virtual checkerboard. Each color represents a single image pose position recorded across two calibrated HMDs and two subjects. The positions represent the relative position of subject relative to the physical image at (0,0) in order to superimpose the virtual checkerboard image. The arc shows the specified distance that the virtual object was rendered at within the HMD, and * symbols show expected positions. Note the bias of measured positions away from the origin.
checkerboard image (red channel only) of known dimensions and capturing its resulting display with a calibrated camera placed at user’s eye position. Twelve different checkerboard poses were captured. The captured images were processed by a corner detection algorithm to generate detected positions for comparison against the known corner positions in the reference images. The corner positions were least-square fit by a geometric transform for all patterns compensate for camera misalignment to produce the error distribution shown, normalized to the checkerboard size (b). Mean, SD of reprojection error was 0.52%±0.31%. An erroneous corner detection result in one of the images caused a single false 6.64% distortion outlier. (c) During human in the loop accuracy testing, a user aligned virtual checkerboard images placed at various orientations with a physical checkerboard poster affixed to a wall at eye level. An optical tracker with clear line of sight to user and target, recorded the position of the user as they moved to align the image. (d) The summary plot shows the results for seven different image poses of the virtual checkerboard. Each color represents a single image pose position recorded across two calibrated HMDs and two subjects. The positions represent the relative position of subject relative to the physical image at (0,0) in order to superimpose the virtual checkerboard image. The arc shows the specified distance that the virtual object was rendered at within the HMD, and * symbols show expected positions. Note the bias of measured positions away from the origin.