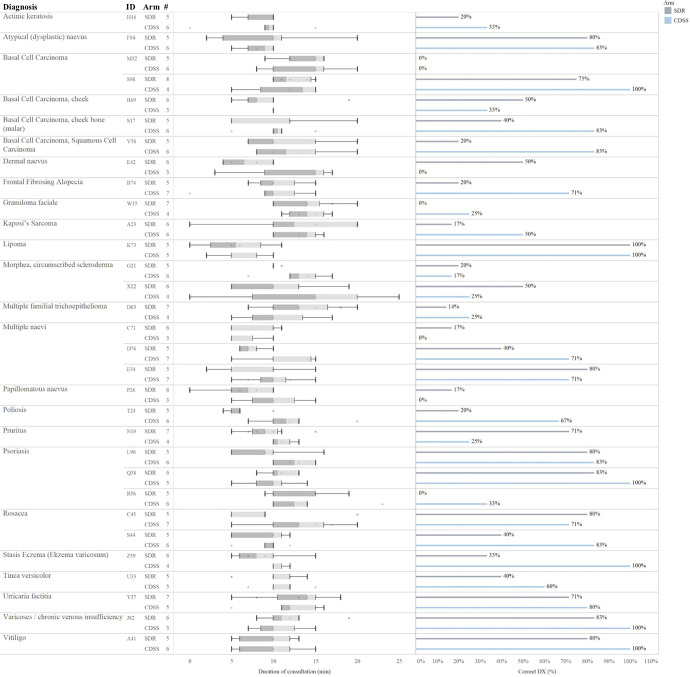
Fig 2. In the majority of consultations CDSS improved the accuracy of the diagnostic outcome.
In total there were 21 different diagnoses. In 65% of the individual cases CDSS resulted in a more correct diagnosis than SDR (20/31 for CDSS, 9/31 for SDR). The following diagnoses received a high correctness in both consultation types (CDSS/SDR): atypical pigmented nävi (83/80), chronic venous insufficiency (100/83), lipoma (100/100), multiple nävi (71/80), psoriasis (83/80), rosacea (71/80), urticaria (80/71), vitiligo (100/80). For eight diagnoses of both consultations type the correctness was poor, that being: actinic keratoses (33/20), BCC (0/0), granuloma faciale (25/0), morphea (17/20, 25/50), multiple nävi (0/17), psoriasis (33/0). The largest difference between the two groups was found in 10 diagnoses: BCC (83/40, 83/20), alopecia (71/20), hereditary kaposi's sarcoma (50/17), morphea (25/50), dermal nevus (0/50), poliosis (67/20), pruritus (25/71), psoriasis (100/71, 33/0), rosacea (83/40), stasis dermatitis [Dermatitis varicosa] (100/33). The consultation duration varied across the different diagnoses as well as the diagnostic accuracy per patient. Consultations lasting less than 2 minutes or more than 20 minutes were considered outliers and excluded from analyses.